The role of organizational citizenship behavior and patriotism in sustaining public health employees' performance
- PMID: 36704689
- PMCID: PMC9872910
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.997643
The role of organizational citizenship behavior and patriotism in sustaining public health employees' performance
Abstract
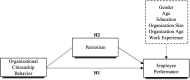
Employee performance during health crises is currently one of the most alarming global concerns. Owing to its significance, scholars assessed factors that improve such performance. However, such improvements in performance require public health employees' discretionary behavior. We investigate the impact of organizational citizenship behavior and patriotism on employee performance, shifting the focus of the healthcare industry's employee performance conversation to how it can be sustained. We used cross-section data from 541 Chinese public health employees who made up the final sample in this study, which has been shown to be appropriate for investigations utilizing a quantitative method. The results of our empirical analysis demonstrate that organizational citizenship behavior positively contributes to sustaining employee performance. We found the same to be true about the positive mediating effect of patriotism on the aforementioned relationship. The findings offer insights into how a country's performance at both local and international levels propels and sustains the job performance of its citizenry. Thus, governments should be more efficient and ensure they maintain a robust institutional environment. This study provides theoretical and empirical evidence based on a research survey of the roles of organizational citizenship behavior and patriotism that sustain employee performance in China's public health sector, in particular during health crises.
Keywords: employee performance; organizational citizenship behavior; patriotism; public health; sustainability.
Copyright © 2023 Rizaie, Horsey, Ge and Ahmad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Aguiar-Quintana T., Nguyen T. H. H., Araujo-Cabrera Y., Sanabria-Díaz J. M. (2021). Do job insecurity, anxiety and depression caused by the COVID-19 pandemic influence hotel employees’ self-rated task performance? The moderating role of employee resilience. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 94:102868. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102868 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angeles Lopez-Cabarcos M., Vazquez-Rodriguez P., Pineiro-Chousa J. (2020). The role of bullying in the development of organizational citizenship behaviors. J. Bus. Res. 115, 272–280. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.10.025 - DOI
-
- Asgari L., Shirkosh S. S., Haghshenas F. (2018). The effect of job burnout on the performance of the employees of the Justice Department (case study: employees of the Justice Department of Alborz Province). Revista Publicando 5, 397–417.
-
- Atatsi E. A., Stoffers J., Kil A. (2019). Factors affecting employee performance: a systematic literature review. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 16, 329–351. doi: 10.1108/JAMR-06-2018-0052 - DOI
-
- Blau P. (1964). Exchange and Power in Social Life. New York: Wiley.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources