Plasma small extracellular vesicles from dogs affected by cutaneous mast cell tumors deliver high levels of miR-21-5p
- PMID: 36704706
- PMCID: PMC9871458
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1083174
Plasma small extracellular vesicles from dogs affected by cutaneous mast cell tumors deliver high levels of miR-21-5p
Abstract
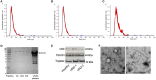
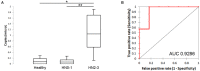
Small extracellular vesicles (sEV) are a class of extracellular vesicles (30-150 nm), delivering molecules including proteins, metabolites, and microRNAs (miRNAs), involved in physiological intercellular crosstalk and disease pathogenesis. The present pilot study aims are (I) to develop an easy and fast protocol for the isolation of sEV from plasma of mast cell tumor (MCT)-affected dogs; (II) to evaluate if miR-21-5p (sEV-miR-21-5p), a miRNA overexpressed by MCT, is associated with sEV. Seventeen dogs have been enrolled in the study: 4 healthy and 13 (6 with and 7 without nodal metastasis) MCT-affected dogs. sEV were isolated using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) (IZON column 35nm) and were characterized by Western blot, Nanoparticle tracking analysis, and transmission electron microscopy. sEV-miR-21-5p was quantified using digital PCR. sEV expressed the specific markers CD9 and TSG101, and a marker of mast cell tryptase. The sEV mean concentration and size were 2.68E + 10 particles/ml, and 99.6 nm, 2.89E + 10 particles/ml and 101.7 nm, and 3.21E + 10 particles/ml and 124 nm in non-metastatic, nodal metastatic, and healthy samples, respectively. The comparative analysis demonstrated that the level of sEV-miR-21-5p was significantly higher in dogs with nodal metastasis compared to healthy (P = 0.038) and without nodal metastasis samples (P = 0.007). In conclusion, the present work demonstrated that a pure population of sEV can be isolated from the plasma of MCT-affected dogs using the SEC approach and that the level of sEV-miR-21-5p is higher in nodal metastatic MCT-affected dogs compared with healthy and MCT-affected dogs without nodal involvement.
Keywords: dog; exosome (vesicle); mast cell tumor; miR-21-5p; size exclusion chromatography.
Copyright © 2023 Zamboni, Zamarian, Stefanello, Ferrari, Auletta, Milanesi, Mauri, Grieco, Ceciliani and Lecchi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum outperforms plasma in small extracellular vesicle microRNA biomarker studies of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 28;26(20):2570-2583. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2570. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32523312 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs derived from plasma small extracellular vesicles predict organo-tropic metastasis of gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2022 Mar;25(2):360-374. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01267-5. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Gastric Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35031872
-
Salivary miR-21 is a potential biomarker for canine mast cell tumors.Vet Pathol. 2023 Jan;60(1):47-51. doi: 10.1177/03009858221128922. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Vet Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36286075
-
Effects of purposeful soccer heading on circulating small extracellular vesicle concentration and cargo.J Sport Health Sci. 2021 Mar;10(2):122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2020.11.006. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Sport Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 33189894 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparative analysis of small extracellular vesicle (sEV) micro-RNA (miRNA) isolation and sequencing procedures in blood plasma samples.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024 Feb 29;5(1):119-137. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.55. eCollection 2024. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024. PMID: 39698410 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Isolation and usage of exosomes in central nervous system diseases.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14677. doi: 10.1111/cns.14677. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38497529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building a Therapeutic Bridge Between Dogs and Humans: A Review of Potential Cross-Species Osteosarcoma Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5152. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115152. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyethylene Glycol -Mediated Exosome Isolation: A Method for Exosomal RNA Analysis.Iran Biomed J. 2024 Mar 1;28(2&3):132-9. doi: 10.61186/ibj.4129. Iran Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 38468372 Free PMC article.
-
First insight into extracellular vesicle-miRNA characterization in a sheep in vitro model of inflammation.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 22;10:1186989. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1186989. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38076552 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Changes in Mastocytes and Their Significance in Mast Cell Tumor Prognosis and Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;15(1):137. doi: 10.3390/genes15010137. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tostes RA, Branco A, Cestari FK, Caleffo T, Viott AD. Retrospective study of canine cutaneous neoplasia. Arch Vet Sci. (2017) 22:71–80. 10.5380/avs.v22i1.49290 - DOI
-
- Ferrari R, Marconato L, Buracco P, Boracchi P, Giudice C, Iussich S, et al. . The impact of extirpation of non-palpable/normal-sized regional lymph nodes on staging of canine cutaneous mast cell tumours: a multicentric retrospective study. Vet Comp Oncol. (2018) 16:505–10. 10.1111/vco.12408 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

