Ameliorative Effects of Vitamins A, C, and E on Sperm Parameters, Testis Histopathology, and Oxidative Stress Status in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle-Treated Rats
- PMID: 36704721
- PMCID: PMC9873442
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/4371611
Ameliorative Effects of Vitamins A, C, and E on Sperm Parameters, Testis Histopathology, and Oxidative Stress Status in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle-Treated Rats
Abstract
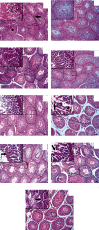
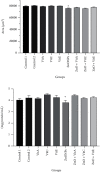
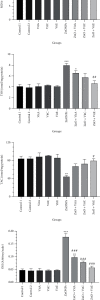
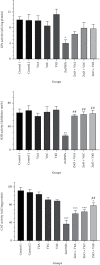
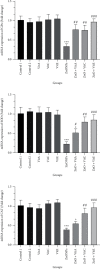
One of the most often utilized nanoparticles (NPs) in several technologies is zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs. However, these NPs are said to have harmful effects on the reproductive system. Thus, we designed this study to specify the potential preventive activity of vitamins (Vits) A, C, and E, as antioxidants, against toxicity of ZnO NPs in the testes of rats. A total of 54 Wistar rats were arranged in 9 groups of 6 and then orally received water (control 1), olive oil (control 2), Vit A (1000 IU/kg), Vit C (200 mg/kg), Vit E (100 IU/kg), ZnO (200 mg/kg), ZnO+Vit A, ZnO+Vit C, and ZnO+Vit E. To determine the amount of testicular injury, sperm analysis and histological evaluation were performed. In addition, oxidative stress status was examined using colorimetric and qRT-PCR methods. Our findings suggest that ZnO NPs cause adverse effects on sperm parameters and testicular histology. Furthermore, oxidative biomarkers (malondialdehyde and total oxidant capacity) were enhanced in the ZnO group. By contrast, the gene expression and activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, GPx, and CAT) noted a remarkable decrease in the ZnO group regarding control (p < 0.05). However, oxidative markers were remarkably mitigated after combined treatment of ZnO NPs and Vits A, C, or E compared to the rats given ZnO NPs (p < 0.05). Additionally, compared to the ZnO NP group, the rats receiving Vits+ZnO NPs exhibit increased antioxidant enzyme activity and mRNA expression (p < 0.05). The findings demonstrate the abovementioned Vits' ameliorative effects on toxicity incurred by ZnO NPs.
Copyright © 2023 Nasrin Ziamajidi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative Effects of Zinc Oxide, in Either Conventional or Nanoformulation, Against Bisphenol A Toxicity on Reproductive Performance, Oxidative Status, Gene Expression and Histopathology in Adult Male Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 May;202(5):2143-2157. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03830-w. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37682394 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of vitamins A, C, and E on zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs)-induced liver oxidative stress in male Wistar rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023 Mar;46(2):209-218. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2021.2016809. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 34915775
-
The antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties of vitamins A, C and E in heart tissue of rats exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2357-2365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08103-8. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36580195
-
The Alleviative Efficacy of Vitamins A, C, and E Against Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles-Induced Hepatic Damage by Reducing Apoptosis in Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Mar;201(3):1252-1260. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03218-2. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35364806
-
The toxicology of ion-shedding zinc oxide nanoparticles.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016;46(4):348-84. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1137864. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26963861 Review.
Cited by
-
Ameliorative Effects of Zinc Oxide, in Either Conventional or Nanoformulation, Against Bisphenol A Toxicity on Reproductive Performance, Oxidative Status, Gene Expression and Histopathology in Adult Male Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 May;202(5):2143-2157. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03830-w. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37682394 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating effect of gallic acid on zinc oxide nanoparticles and arsenic trioxide-induced spermatogenesis suppression, testicular injury, hormonal imbalance, and immunohistochemical changes in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;397(12):9859-9875. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03228-y. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38935127 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of oxidative stress-induced sperm dysfunction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 5;16:1520835. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1520835. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39974821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating the RFamide-related peptide-3/G protein-coupled receptor 147 signaling pathway with nourishing Yin-removing fire herbal mixture to alleviate precocious puberty in female rats: An experimental study.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2024 Feb 23;22(1):31-42. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v22i1.15240. eCollection 2024 Jan. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38544669 Free PMC article.
-
Cell protective effects of vitamin C against oxidative stress induced by ciprofloxacin on spermatogenesis: involvement of cellular apoptosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 20;13:1489959. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1489959. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40196846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Syama S., Reshma S., Sreekanth P., Varma H., Mohanan P. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on cellular oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanisms in mouse liver. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry . 2013;95(3):495–503. doi: 10.1080/02772248.2013.789606. - DOI
-
- Salman R. A. Histopathological effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Kkidney and liver tissues in albino male mice. Ibn AL-Haitham Journal For Pure and Applied Sciences . 2018;31(1):9–14. doi: 10.30526/31.1.1844. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

