α‑hederin overcomes hypoxia‑mediated drug resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting the AKT/Bcl2 pathway
- PMID: 36704835
- PMCID: PMC9911077
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5481
α‑hederin overcomes hypoxia‑mediated drug resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting the AKT/Bcl2 pathway
Abstract
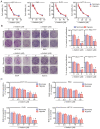
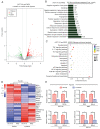
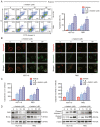
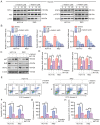
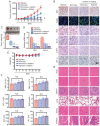
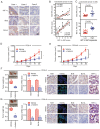
Currently, chemoresistance is a major challenge that directly affects the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). In addition, hypoxia is associated with poor prognosis and therapeutic resistance in patients with cancer. Accumulating evidence has shown that α‑hederin has significant antitumour effects and that α‑hederin can inhibit hypoxia‑mediated drug resistance in CRC; however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In the present study, viability and proliferation assays were used to evaluate the effect of α‑hederin on the drug resistance of CRC cells under hypoxia. Sequencing analysis and apoptosis assays were used to determine the effect of α‑hederin on apoptosis under hypoxia. Western blot analysis and reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR were used to measure apoptosis‑related protein and mRNA expression levels. Furthermore, different mouse models were established to study the effect of α‑hederin on hypoxia‑mediated CRC drug resistance in vivo. In the present study, the high expression of Bcl2 in hypoxic CRC cells was revealed to be a key factor in their drug resistance, whereas α‑hederin inhibited the expression of Bcl2 by reducing AKT phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo, and promoted the apoptosis of CRC cells under hypoxia. By contrast, overexpression of AKT reversed the effect of α‑hederin on CRC cell apoptosis under hypoxia. Taken together, these results suggested that α‑hederin may overcome hypoxia‑mediated drug resistance in CRC by inhibiting the AKT/Bcl2 pathway. In the future, α‑hederin may be used as a novel adjuvant for reversing drug resistance in CRC.
Keywords: Bcl2; CRC; chemoresistance; hypoxia; α‑hederin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hedyotis diffusa Willd inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of 5‑FU resistant colorectal cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):358-365. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7903. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115462
-
Hypoxia Induces Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer through the HIF-1α/miR-338-5p/IL-6 Feedback Loop.Mol Ther. 2019 Oct 2;27(10):1810-1824. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.05.017. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31208913 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin has a better effect on PIK3CA mutant colorectal cancer cells by PI3K/Akt/Raptor pathway.Mol Med. 2020 Jan 30;26(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-0139-5. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32000660 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of microRNA-135b and microRNA-182 promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by targeting ST6GALNAC2 via PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Dec;56(12):2669-2680. doi: 10.1002/mc.22710. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28767179
-
The measurement and modification of hypoxia in colorectal cancer: overlooked but not forgotten.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2022 Aug 25;10:goac042. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goac042. eCollection 2022. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 36032656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accumulation differences of high-value ingredients in different phenotype Lonicera macranthoides: insights from integrative metabolome and transcriptome analyses.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 4;16:1533263. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1533263. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40104033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang M, Liu Q, Li L, Ning J, Tu J, Lei X, Mo Z, Tang S. Cytoplasmic M-CSF facilitates apoptosis resistance by inhibiting the HIF-1α/BNIP3/Bax signalling pathway in MCF-7 cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41:1807–1816. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
