Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS-CoV-2-related mortality in mice
- PMID: 36704839
- PMCID: PMC10014049
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13771
Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS-CoV-2-related mortality in mice
Abstract
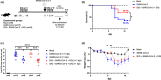
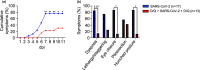
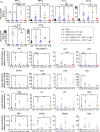
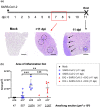
The enormous societal impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has been particularly harsh for some social groups, such as the elderly. Recently, it has been suggested that senescent cells could play a central role in pathogenesis by exacerbating the pro-inflammatory immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, the selective clearance of senescent cells by senolytic drugs may be useful as a therapy to ameliorate the symptoms of COVID-19 in some cases. Using the established COVID-19 murine model K18-hACE2, we demonstrated that a combination of the senolytics dasatinib and quercetin (D/Q) significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2-related mortality, delayed its onset, and reduced the number of other clinical symptoms. The increase in senescent markers that we detected in the lungs in response to SARS-CoV-2 may be related to the post-COVID-19 sequelae described to date. These results place senescent cells as central targets for the treatment of COVID-19, and make D/Q a new and promising therapeutic tool.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cellular senescence; senolytics; survival.
© 2023 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
C.V.K. declares that he is co‐founder of SenCell Therapeutics S.L.
Figures
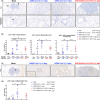
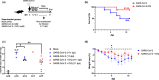
References
-
- Boumaza, A. , Gay, L. , Mezouar, S. , Bestion, E. , Diallo, A. B. , Michel, M. , Desnues, B. , Raoult, D. , la Scola, B. , Halfon, P. , Vitte, J. , Olive, D. , & Mege, J. L. (2021). Monocytes and macrophages, targets of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: The clue for coronavirus disease 2019 immunoparalysis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 224, 395–406. 10.1093/infdis/jiab044 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camell, C. D. , Yousefzadeh, M. J. , Zhu, Y. , Prata, L. G. P. L. , Huggins, M. A. , Pierson, M. , Zhang, L. , O'Kelly, R. D. , Pirtskhalava, T. , Xun, P. , Ejima, K. , Xue, A. , Tripathi, U. , Espindola‐Netto, J. M. , Giorgadze, N. , Atkinson, E. J. , Inman, C. L. , Johnson, K. O. , Cholensky, S. H. , … Robbins, P. D. (2021). Senolytics reduce coronavirus‐related mortality in old mice. Science, 373, eabe4832. 10.1126/science.abe4832 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. , Lau, Y. F. , Lamirande, E. W. , Paddock, C. D. , Bartlett, J. H. , Zaki, S. R. , & Subbarao, K. (2010). Cellular immune responses to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS‐CoV) infection in senescent BALB/c mice: CD4 + T cells are important in control of SARS‐CoV infection. Journal of Virology, 84, 1289–1301. 10.1128/jvi.01281-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

