Supporting early-career women researchers: lessons from a global mentorship programme
- PMID: 36705071
- PMCID: PMC9888473
- DOI: 10.1080/16549716.2022.2162228
Supporting early-career women researchers: lessons from a global mentorship programme
Abstract
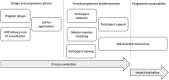
Mentorship is an important contributor to strengthening research capacity among health researchers. Formal mentorship programmes, targeting women mentees can help mitigate some of the gendered power dynamics and can also help early career researchers learn from others' experiences of navigating these challenges. In 2020, the UNDP/UNFPA/UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction at the World Health Organization launched a mentorship programme geared towards early career women researchers. This paper describes the process of designing and implementing a mentorship programme for early career women sexual and reproductive health and rights researchers from low- and middle-income countries including valuable lessons learned vis-à-vis existing evidence. Some of these findings have been incorporated into iterations of the programme launched in 2022. Critical points include: ensuring considerations for language and geographical distribution; allowing mentees to participate in the matching process; providing training and opportunities to network and learn from other participants; offering the support and structure for developing these relationships. Providing women researchers with the tools - through mentorship - to navigate the unique challenges they face in their career journeys, can have a lasting impact on research capacity. Countries and institutions committed to strengthening research capacity need to focus on the holistic growth and motivation of individuals in a way that ensures gender equality.
Keywords: Mentorship; low and middle income countries (LMICs); research; research capacity strengthening; sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR); women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors were all employed with HRP at the time of developing and implementing the programme, and of preparing this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources