3D-EPI blip-up/down acquisition (BUDA) with CAIPI and joint Hankel structured low-rank reconstruction for rapid distortion-free high-resolution mapping
- PMID: 36705076
- PMCID: PMC10072851
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29578
3D-EPI blip-up/down acquisition (BUDA) with CAIPI and joint Hankel structured low-rank reconstruction for rapid distortion-free high-resolution mapping
Abstract
Purpose: This work aims to develop a novel distortion-free 3D-EPI acquisition and image reconstruction technique for fast and robust, high-resolution, whole-brain imaging as well as quantitative mapping.
Methods: 3D Blip-up and -down acquisition (3D-BUDA) sequence is designed for both single- and multi-echo 3D gradient recalled echo (GRE)-EPI imaging using multiple shots with blip-up and -down readouts to encode B0 field map information. Complementary k-space coverage is achieved using controlled aliasing in parallel imaging (CAIPI) sampling across the shots. For image reconstruction, an iterative hard-thresholding algorithm is employed to minimize the cost function that combines field map information informed parallel imaging with the structured low-rank constraint for multi-shot 3D-BUDA data. Extending 3D-BUDA to multi-echo imaging permits mapping. For this, we propose constructing a joint Hankel matrix along both echo and shot dimensions to improve the reconstruction.
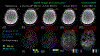
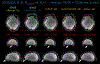
Results: Experimental results on in vivo multi-echo data demonstrate that, by performing joint reconstruction along with both echo and shot dimensions, reconstruction accuracy is improved compared to standard 3D-BUDA reconstruction. CAIPI sampling is further shown to enhance image quality. For mapping, parameter values from 3D-Joint-CAIPI-BUDA and reference multi-echo GRE are within limits of agreement as quantified by Bland-Altman analysis.
Conclusions: The proposed technique enables rapid 3D distortion-free high-resolution imaging and mapping. Specifically, 3D-BUDA enables 1-mm isotropic whole-brain imaging in 22 s at 3T and 9 s on a 7T scanner. The combination of multi-echo 3D-BUDA with CAIPI acquisition and joint reconstruction enables distortion-free whole-brain mapping in 47 s at 1.1 × 1.1 × 1.0 mm3 resolution.
Keywords:
© 2023 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Wei-Ching Lo is a Staff Scientist at Siemens Healthineers, USA.
Figures
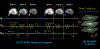
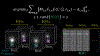
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional echo-shifted EPI with simultaneous blip-up and blip-down acquisitions for correcting geometric distortion.Magn Reson Med. 2023 Dec;90(6):2375-2387. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29828. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Magn Reson Med. 2023. PMID: 37667533 Free PMC article.
-
Blip up-down acquisition for spin- and gradient-echo imaging (BUDA-SAGE) with self-supervised denoising enables efficient T2 , T2 *, para- and dia-magnetic susceptibility mapping.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Aug;88(2):633-650. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29219. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 35436357
-
Efficient T2 mapping with blip-up/down EPI and gSlider-SMS (T2 -BUDA-gSlider).Magn Reson Med. 2021 Oct;86(4):2064-2075. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28872. Epub 2021 May 28. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 34046924 Free PMC article.
-
Distortion-free, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion MRI with gSlider BUDA-EPI and multicoil dynamic B0 shimming.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Aug;86(2):791-803. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28748. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33748985 Free PMC article.
-
Echo planar time-resolved imaging (EPTI).Magn Reson Med. 2019 Jun;81(6):3599-3615. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27673. Epub 2019 Feb 3. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30714198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spherical echo-planar time-resolved imaging (sEPTI) for rapid 3D quantitative and susceptibility imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Jan;93(1):121-137. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30255. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39250435 Free PMC article.
-
PixCUE: Joint Uncertainty Estimation and Image Reconstruction in MRI using Deep Pixel Classification.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Aug;38(4):2071-2084. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01250-3. Epub 2024 Dec 4. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39633210 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional echo-shifted EPI with simultaneous blip-up and blip-down acquisitions for correcting geometric distortion.Magn Reson Med. 2023 Dec;90(6):2375-2387. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29828. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Magn Reson Med. 2023. PMID: 37667533 Free PMC article.
-
A new 3D phase unwrapping method by region partitioning and local polynomial modeling in abdominal quantitative susceptibility mapping.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 15;17:1287788. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1287788. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38033538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gracien RM, Maiworm M, Brüche N, et al. How stable is quantitative MRI? – Assessment of intra- and inter-scanner-model reproducibility using identical acquisition sequences and data analysis programs. Neuroimage 2020; 207: 1–11. - PubMed
-
- van Wijnen A, Petrov F, Maiworm M, et al. Cortical quantitative MRI parameters are related to the cognitive status in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur. Radiol 2020; 30: 1045–1053. - PubMed
-
- Bandettini PA. Twenty years of functional MRI: The science and the stories. Neuroimage 2012; 62: 575–588. - PubMed
-
- Liao C, Cao X, Cho J, Zhang Z, Setsompop K, Bilgic B. Highly efficient MRI through multi-shot echo planar imaging. Wavelets and Sparsity XVIII. Vol. 11138. Bellingham, WA: SPIE; 2019: 43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

