The long noncoding RNA Meg3 mediates TLR4-induced inflammation in experimental obstructive nephropathy
- PMID: 36705251
- PMCID: PMC9977690
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20220537
The long noncoding RNA Meg3 mediates TLR4-induced inflammation in experimental obstructive nephropathy
Abstract
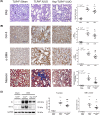
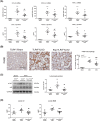
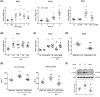
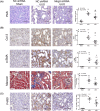
Kidney inflammation contributes to the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Modulation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling is a potential therapeutic strategy for this pathology, but the regulatory mechanisms of TLR4 signaling in kidney tubular inflammation remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that tubule-specific deletion of TLR4 in mice conferred protection against obstruction-induced kidney injury, with reduction in inflammatory cytokine production, macrophage infiltration and kidney fibrosis. Transcriptome analysis revealed a marked down-regulation of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Meg3 in the obstructed kidney from tubule-specific TLR4 knockout mice compared with wild-type control. Meg3 was also induced by lipopolysaccharide in tubular epithelial cells via a p53-dependent signaling pathway. Silencing of Meg3 suppressed LPS-induced cytokine production of CCL-2 and CXCL-2 and the activation of p38 MAPK pathway in vitro and ameliorated kidney fibrosis in mice with obstructive nephropathy. Together, these findings identify a proinflammatory role of lncRNA Meg3 in CKD and suggest a novel regulatory pathway in TLR4-driven inflammatory responses in tubular epithelial cells.
Keywords: Meg3; TLR4 signaling; kidney fibrosis; large intervening non-coding RNA; tubular injury.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA MEG3: an active player in fibrosis.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Feb;77(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00661-x. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39373865 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes fibrosis and inflammatory response in diabetic nephropathy via miR-181a/Egr-1/TLR4 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Jun 13;11(11):3716-3730. doi: 10.18632/aging.102011. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31195367 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA MEG3 protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice through miR-93-5p-dependent inhibition of NF‑κB signaling pathway.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Nov;239:154142. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154142. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36242967
-
Toll-like receptor 4 promotes tubular inflammation in diabetic nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jan;23(1):86-102. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010111210. Epub 2011 Oct 21. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22021706 Free PMC article.
-
The role of long noncoding RNA MEG3 in fibrosis diseases.Postgrad Med J. 2024 Jul 18;100(1186):529-538. doi: 10.1093/postmj/qgad124. Postgrad Med J. 2024. PMID: 38430191 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA transcripts in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-host interactions.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Dec 15;11:281-293. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.12.005. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39926616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA MEG3: an active player in fibrosis.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Feb;77(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00661-x. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39373865 Review.
-
S100 calcium-binding protein A9 promotes skin regeneration through toll-like receptor 4 during tissue expansion.Burns Trauma. 2023 Oct 31;11:tkad030. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkad030. eCollection 2023. Burns Trauma. 2023. PMID: 37936894 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MEG3: Targeting the Molecular Mechanisms and Pathogenic causes of Metabolic Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(37):6140-6153. doi: 10.2174/0109298673268051231009075027. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37855346 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: key regulators of liver and kidney fibrogenesis.BMB Rep. 2023 Jul;56(7):374-384. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0075. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37357534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

