Risk of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in intermediate-risk regimens: Clinical and economic outcomes of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor prophylaxis
- PMID: 36705281
- PMCID: PMC10387928
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2023.29.2.128
Risk of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in intermediate-risk regimens: Clinical and economic outcomes of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor prophylaxis
Abstract
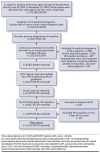
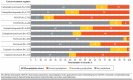
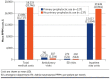
BACKGROUND: Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia increases the risk of febrile neutropenia (FN) and infection with resultant hospitalizations, with substantial health care resource utilization (HCRU) and costs. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (GCSF) is recommended as primary prophylaxis for chemotherapy regimens having more than a 20% risk of FN. Yet, for intermediate-risk (10%-20%) regimens, it should be considered only for patients with 1 or more clinical risk factors (RFs) for FN. It is unclear whether FN prophylaxis for intermediate-risk patients is being optimally implemented. OBJECTIVE: To examine RFs, prophylaxis use, HCRU, and costs associated with incident FN during chemotherapy. METHODS: This retrospective study used administrative claims data for commercial and Medicare Advantage enrollees with nonmyeloid cancer treated with intermediate-risk chemotherapy regimens during January 1, 2009, to March 31, 2020. Clinical RFs, GCSF prophylaxis, incident FN, HCRU, and costs were analyzed descriptively by receipt of primary GCSF, secondary GCSF, or no GCSF prophylaxis. Multivariable Cox regression analysis was used to examine the association between number of RFs and cumulative FN risk. RESULTS: The sample comprised 13,937 patients (mean age 67 years, 55% female). Patients had a mean of 2.3 RFs, the most common being recent surgery, were aged 65 years or greater, and had baseline liver or renal dysfunction; 98% had 1 or more RFs. However, only 35% of patients received primary prophylaxis; 12% received secondary prophylaxis. The hazard ratio of incident FN was higher with increasing number of RFs during the first line of therapy, yet more than 54% of patients received no prophylaxis, regardless of RFs. Use of GCSF prophylaxis varied more by chemotherapeutic regimen than by number of RFs. Among patients treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride (doxorubicin hydrochloride), vincristine, and prednisone, 76% received primary prophylaxis, whereas only 22% of patients treated with carboplatin/paclitaxel received primary prophylaxis. Among patients with a first line of therapy FN event, 78% had an inpatient stay and 42% had an emergency visit. During cycle 1, mean FN-related coordination of benefits-adjusted medical costs per patient per month ($13,886 for patients with primary prophylaxis and $18,233 for those with none) were driven by inpatient hospitalizations, at 91% and 97%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: Incident FN occurred more often with increasing numbers of RFs, but GCSF prophylaxis use did not rise correspondingly. Variation in prophylaxis use was greater based on regimen than RF number. Lower health care costs were observed among patients with primary prophylaxis use. Improved individual risk identification for intermediate-risk regimens and appropriate prophylaxis may decrease FN events toward the goal of better clinical and health care cost outcomes. DISCLOSURES: This work was funded by Sandoz Inc., which participated in the design of the study, interpretation of the data, writing and revision of the manuscript, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The study was performed by Optum under contract with Sandoz Inc. The author(s) meet criteria for authorship as recommended by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. The authors received no direct compensation related to the development of the manuscript. Dr Li is an employee of Sandoz Inc. Drs Bell and Lal and Mr Peterson-Brandt were employees of Optum at the time of the study. Ms Anderson and Dr Aslam are employees of Optum. Dr Lyman has been primary investigator on a research grant from Amgen to their institution and has consulted for Sandoz, G1 Therapeutics, Partners Healthcare, BeyondSpring, ER Squibb, Merck, Jazz Pharm, Kallyope, Teva; Fresenius Kabi, Seattle Genetics, and Samsung.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by Sandoz Inc., which participated in the design of the study, interpretation of the data, writing and revision of the manuscript, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The study was performed by Optum under contract with Sandoz Inc. The author(s) meet criteria for authorship as recommended by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. The authors received no direct compensation related to the development of the manuscript. Dr Li is an employee of Sandoz Inc. Drs Bell and Lal and Mr Peterson-Brandt were employees of Optum at the time of the study. Ms Anderson and Dr Aslam are employees of Optum. Dr Lyman has been primary investigator on a research grant from Amgen to their institution and has consulted for Sandoz, G1 Therapeutics, Partners Healthcare, BeyondSpring, ER Squibb, Merck, Jazz Pharm, Kallyope, Teva; Fresenius Kabi, Seattle Genetics, and Samsung.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Outcomes of Treatment with Filgrastim Versus a Filgrastim Biosimilar and Febrile Neutropenia-Associated Costs Among Patients with Nonmyeloid Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Oct;24(10):976-984. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.17447. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29687743 Free PMC article.
-
Primary prophylaxis with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) reduces the incidence of febrile neutropenia in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) receiving CHOP chemotherapy treatment without adversely affecting their quality of life: cost-benefit and quality of life analysis.Support Care Cancer. 2013 Mar;21(3):841-6. doi: 10.1007/s00520-012-1589-2. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Support Care Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22972488
-
A retrospective analysis of nadir-neutropenia directed pegylated granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on febrile neutropenia rates in (neo)adjuvant breast cancer chemotherapy regimens.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020 Oct;3(5):e1266. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1266. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32761893 Free PMC article.
-
2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2011 Jan;47(1):8-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.10.013. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Eur J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21095116
-
The risk of febrile neutropenia and need for G-CSF primary prophylaxis with the docetaxel and cyclophosphamide regimen in early-stage breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;153(3):591-7. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3531-z. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26337685 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (FN): healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and costs in commercially insured patients in the US.Support Care Cancer. 2024 May 23;32(6):373. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08492-5. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38777864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartzberg LS, Lal LS, Balu S, et al. . Clinical outcomes of treatment with filgrastim versus a filgrastim biosimilar and febrile neutropenia-associated costs among patients with nonmyeloid cancer undergoing chemotherapy. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018;24(1):976-84. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2018.17447 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liutkauskiene S, Grizas S, Jureniene K, Suipyte J, Statnickaite A, Juozaityte E. Retrospective analysis of the impact of anthracycline dose reduction and chemotherapy delays on the outcomes of early breast cancer molecular subtypes. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):453. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4365-y - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denduluri N, Patt DA, Wang Y, et al. . Dose delays, dose reductions, and relative dose intensity in patients with cancer who received adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy in community oncology practices. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2015;13(11):1383-93. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2015.0166 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous