Diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography for endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36705368
- PMCID: PMC9875999
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032700
Diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography for endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This meta-analysis aimed to identify the accuracy of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer (EC).
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Cochrane Library, and chinese biomedical literature database from inception to September 30, 2022. Meta-analysis was conducted using STATA version 14.0 and Meta-Disc version 1.4 software. We calculated summary statistics for sensitivity (Sen), specificity (Spe), positive and negative likelihood ratio (LR+/LR-), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves.
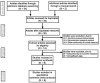
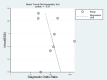
Results: Eight studies that met all the inclusion criteria were included in this meta-analysis. A total of 432 patients with EC and 548 with benign endometrial lesions were assessed. All endometrial lesions were histologically confirmed by SWE. The pooled Sen was 0.91 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.83-0.95); the pooled Spe was 0.90 (95% CI = 0.86-0.93); the pooled LR+ was 9.10 (95% CI = 6.20-13.35); the pooled negative LR- was 0.10 (95% CI = 0.05-0.20); the pooled DOR of SWE in the diagnosis of EC was 90.73 (95% CI = 36.62-804.5). The area under the SROC curve was 0.95 (95% CI = 0.93-0.97). No evidence of publication bias was found (t = 0.98, P = .37).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis indicates that SWE may have high diagnostic accuracy in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant endometrial lesions. Thus, SWE may be a useful tool for the diagnosis of EC.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with shear wave elastography in differentiating benign from malignant breast lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gland Surg. 2023 Nov 24;12(11):1610-1623. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-333. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 38107493 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the accuracy of shear wave elastography and strain elastography in the diagnosis of breast tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 4;101(44):e31526. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031526. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36343055 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound superb microvascular imaging for breast tumor: a meta-analysis.Med Ultrason. 2020 Sep 5;22(3):313-318. doi: 10.11152/mu-2460. Med Ultrason. 2020. PMID: 32898204
-
Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jul;35(7):6343-50. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1815-2. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24659450
-
Is Diagnostic Performance of Quantitative 2D-Shear Wave Elastography Optimal for Clinical Classification of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules?: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2022 Mar;29 Suppl 3:S114-S121. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 29054676
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Doll KM, Winn AN. Assessing endometrial cancer risk among US women: long-term trends using hysterectomy-adjusted analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:318.e1–9. - PubMed
-
- Bouzid A, Ayachi A, Mourali M. Value of ultrasonography to predict the endometrial cancer in postmenopausal bleeding. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2015;43:652–8. - PubMed
-
- Ophir J, Garra B, Kallel F, et al. . Elastographic imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2000;26(Suppl. 1):S23–9. - PubMed
-
- Garra BS. Imaging and estimation of tissue elasticity by ultrasound. Ultrasound Q. 2007;23:255–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

