Analysis of risk factors of fungal superinfections in viral pneumonia patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36705416
- PMCID: PMC9804449
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.760
Analysis of risk factors of fungal superinfections in viral pneumonia patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Infections with fungi, such as Aspergillus species, have been found as common complications of viral pneumonia. This study aims to determine the risk factors of fungal superinfections in viral pneumonia patients using meta-analysis.
Objective: This study aims to determine the risk factors of fungal infection s in viral pneumonia patients using meta-analysis.
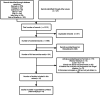
Methods: We reviewed primary literature about fungal infection in viral pneumonia patients published between January 1, 2010 and September 30, 2020, in the Chinese Biomedical Literature, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang (China), Cochrane Central Library, Embase, PubMed, and Web of Science databases. These studies were subjected to an array of statistical analyses, including risk of bias and sensitivity analyses.
Results: In this study, we found a statistically significant difference in the incidence of fungal infections in viral pneumonia patients that received corticosteroid treatment as compared to those without corticosteroid treatment (p < .00001). Additionally, regarding the severity of fungal infections, we observed significant higher incidence of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) in patients with high Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II scores (p < .001), tumors (p = .005), or immunocompromised patients (p < .0001).
Conclusions: Our research shows that corticosteroid treatment was an important risk factor for the development of fungal infection in patients with viral pneumonia. High APACHE II scores, tumors, and immunocompromised condition are also important risk factors of developing IPA. The diagnosis of fungal infection in viral pneumonia patients can be facilitated by early serum galactomannan (GM) testing, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid Aspergillus antigen testing, culture, and biopsy.
Keywords: IPA; corticosteroid; fungal infection; systematic review and meta-analysis; viral pneumonia.
© 2022 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Evaluation of risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and detection of diagnostic values of galactomannan and PCR methods in bronchoalveolar lavage samples from non-neutropenic intensive care unit patients].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015 Oct;49(4):565-75. doi: 10.5578/mb.9906. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015. PMID: 26649414 Turkish.
-
Comparison of 1,3-β-d-glucan with galactomannan in serum and bronchoalveolar fluid for the detection of Aspergillus species in immunosuppressed mechanical ventilated critically ill patients.J Crit Care. 2016 Dec;36:259-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.06.026. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27475024
-
Diagnostic yield of a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan assay in patients with negative serum galactomannan results suspected to have invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.Mycoses. 2021 Sep;64(9):1124-1131. doi: 10.1111/myc.13269. Epub 2021 May 24. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33740824
-
Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan assay for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in adults: A meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):1913-1922. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13792. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36324286 Review.
-
Serology anno 2021-fungal infections: from invasive to chronic.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Sep;27(9):1230-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.005. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33601011 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulatory Inflammatory Proteins as Early Diagnostic Biomarkers for Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies-an Exploratory Study.Mycopathologia. 2024 Feb 26;189(2):24. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00831-8. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38407673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang JW, Fan LC, Miao XY, et al. Corticosteroids for the treatment of human infection with influenza virus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(10):956‐963. - PubMed
-
- Ma YB, Zhang Y, Huang C, Wang XW, Li RY. Research progress of natural killer cells in fungal infection immunity. J Chinese Journal of Mycology. 2020;15(3):175‐178.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

