Comparative evaluation of the health utilities index mark 3 and the short form 6D: evidence from an individual participant data meta-analysis of very preterm and very low birthweight adults
- PMID: 36705795
- PMCID: PMC10172285
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-023-03344-x
Comparative evaluation of the health utilities index mark 3 and the short form 6D: evidence from an individual participant data meta-analysis of very preterm and very low birthweight adults
Abstract
Background: The most appropriate preference-based health-related quality of life (HRQoL) instruments for trials or research studies that ascertain the consequences of individuals born very preterm and/or low birthweight (VP/VLBW) are not known. Agreement between the HUI3 and SF-6D multi-attribute utility measures have not been previously investigated for VP/VLBW and normal birthweight or term-born controls. This study examined the agreement between the outputs of the HUI3 and SF-6D measures among adults born VP/VLBW and normal birthweight or term born controls.
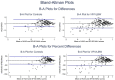
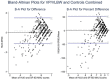
Methods: We used two prospective cohorts of individuals born VP/VLBW and controls contributing to the 'Research on European Children and Adults Born Preterm' (RECAP) consortium which assessed HRQoL using two preference-based measures. The combined dataset of individual participant data (IPD) included 407 adult VP/VLBW survivors and 367 controls, ranging in age from 18 to 26 years. Bland-Altman plots, intra-class correlation coefficients, and generalized linear mixed models in a one-step approach were used to examine agreement between the measures.
Results: There was significant discordance between the HUI3 and SF-6D multi-attribute utility measures in the VP/VLBW sample, controls, and in the combined samples. Agreement between the HUI3 and SF-6D multi-attribute utility measures was weaker in controls compared with VP/VLBW individuals.
Conclusions and relevance: The HUI3 and SF-6D each provide unique information on different aspects of health status across the groups. The HUI3 better captures preterm-related changes to HRQoL in adulthood compared to SF-6D. Studies focused on measuring physical or cognitive aspects of health will likely benefit from using the HUI3 instead of the SF-6D, regardless of gestational age at birth and birthweight status.
Keywords: HRQoL; HUI3; Health utilities; SF-6D; Very low birth weight; Very preterm birth.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Drummond Michael F, Sculpher Mark J, Karl Claxton, Stoddart Greg L, Torrance George W. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford University Press; 2015.
-
- Drugs Canadian Agency, Health Technologies, others. (2006). Guidelines for the economic evaluation of health technologies: Canada.
-
- Excellence Care. Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal, Retrieved April 4, 2013, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395867/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK395867.pdf - PubMed
-
- Stenman U, Hakama M, Knekt P, et al. Measurement and modeling of health-related quality of life. Epidemiology Demography Public Health. 2010;195:130–135.
-
- Human Services Australia. Dept., Health. (1995). Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Industry on Preparation of Submissions to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee: Including Major Submissions Involving Economic Analyses, November 1995. Australian Government Pub. Service.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources