The Development of STING Agonists and Emerging Results as a Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 36705879
- PMCID: PMC10994474
- DOI: 10.1007/s11912-023-01361-0
The Development of STING Agonists and Emerging Results as a Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
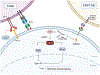
Purpose of review: New therapies are needed to potentiate the effects of current immunotherapies and overcome resistance. The stimulator of interferon genes genes (STING) pathway is an innate immune activating cascade that may enhance current cancer immunotherapies.
Recent findings: Preclinical data has shown that the addition of a STING agonist enhances the effect of current treatments such as immune checkpoint inhibitor antibodies and radiation therapy. Early phase trials have demonstrated modest efficacy of STING agonists and revealed new mechanistic and technical challenges. STING agonists are a new class of agents that activate the immune response to improve tumor control. A wide range of preclinical experiments, translational data, and ongoing clinical trials support the therapeutic use of STING agonists in patients. Trials to determine optimal drug combinations and novel delivery mechanisms are continuing in development.
Keywords: Anti-tumor immunity; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immunotherapy; Innate immune activation; STING agonist; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

