Developing a fall prevention intervention economic model
- PMID: 36706109
- PMCID: PMC9882648
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280572
Developing a fall prevention intervention economic model
Abstract
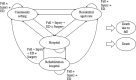
Purpose: Model-based economic evaluations require conceptualization of the model structure. Our objectives were to identify important health states, events, and patient attributes to be included in a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis of fall prevention interventions, to develop a model structure to examine cost-effectiveness of fall prevention interventions, and to assess the face validity of the model structure.
Methods: An expert panel comprising clinicians, health service researchers, health economists, a patient partner, and policy makers completed two rounds of online surveys to gain consensus on health states, events, and patient attributes important for fall prevention interventions. The surveys were informed by a literature search on fall prevention interventions for older adults (≥65 years) including economic evaluations and clinical practice guidelines. The results of the Delphi surveys and subsequent discussions can support the face validity of a state-transition model for an economic evaluation of fall prevention interventions.
Results: In total, 11 experts rated 24 health states/events and 41 patient attributes. Consensus was achieved on 14 health states/events and 26 patient characteristics. The proposed model structure incorporated 12 of the 14 selected health states/events. Panelists confirmed the face validity of the model structure during teleconferences.
Conclusions: There is a dearth of studies presenting the model conceptualization process; consequently, this study involving multiple end user partners with opportunities for input at several stages adds to the literature as another case study. This process is an example of how a fall prevention economic model was developed using a modified Delphi process and assessed for face validity.
Copyright: © 2023 Saunders et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- The Canadian Press. Falls the main reason seniors head to hospital, CIHI injury report indicates: CBC; 2019 [July 12, 2019]. Available from: https://www.cbc.ca/news/health/falls-seniors-cihi-1.5208253.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

