Effect of matrine in MAC-T cells and their transcriptome analysis: A basic study
- PMID: 36706149
- PMCID: PMC9882957
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280905
Effect of matrine in MAC-T cells and their transcriptome analysis: A basic study
Abstract
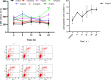
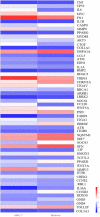
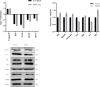
Matrine, an alkaloid derived from herbal medicine, has a wide range of biological activities, including antibacterial. Matrine was toxic to multiple cells at high concentrations. Bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T) could be used as model cells for cow breast. Matrine was a feasible option to replace antibiotics in the prevention or treatment of mastitis against the background of prohibiting antibiotics, but the safe concentration of matrine on MAC-T cells and the mechanism of action for matrine at different concentrations were still unclear. In this study, different concentrations of matrine (0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 mg/mL) were used to treat MAC-T cells for various time periods (4, 8, 12, 16 and 24 h) and measure their lactic dehydrogenase (LDH). And then the optimal doses (2 mg/mL) were chosen to detect the apoptosis at various time periods by flow cytometry and transcriptome analysis was performed between the control and 2 mg/mL matrine-treated MAC-T cells for 8 hours. The results showed that matrine was not cytotoxic at 0.5 mg/mL, but it was cytotoxic at 1~3 mg/mL. In addition, matrine induced apoptosis in MAC-T cells at 2 mg/mL and the proportion of apoptosis cells increases with time by flow cytometry. RNA-seq analysis identified 1645 DEGs, 676 of which were expressed up-regulated and 969 were expressed down-regulated. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis indicated the following pathways were linked to matrine-induced toxicity and apoptosis, including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway, viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, P53 and PPAR pathway. We found 7 DEGs associated with matrine toxicity and apoptosis. This study would provide a basis for the safety of matrine in the prevention or treatment of mastitis.
Copyright: © 2023 Zhang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of antitumor agent matrine on FOXO and PI3K-AKT pathway in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.Sci China Life Sci. 2018 May;61(5):550-558. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-9050-6. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29119376
-
Effects of matrine on proliferation and apoptosis of cultured retinoblastoma cells.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012 Jun;250(6):897-905. doi: 10.1007/s00417-011-1751-4. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 21866335
-
Matrine and baicalin inhibit apoptosis induced by Panton-Valentine leukocidin of Staphylococcus aureus in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Mar;103(3):2731-2742. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17619. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 31954568
-
Illumination of Molecular Pathways in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions and the Immune Mechanism of Matrine Treatment in EAE, a Mouse Model of MS.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 12;12:640778. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640778. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33912166 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances on anticancer activities of matrine and its derivatives: An updated overview.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jan 1;161:205-238. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.10.037. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30359819 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

