Ionizable lipid nanoparticles deliver mRNA to pancreatic β cells via macrophage-mediated gene transfer
- PMID: 36706177
- PMCID: PMC9882987
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade1444
Ionizable lipid nanoparticles deliver mRNA to pancreatic β cells via macrophage-mediated gene transfer
Abstract
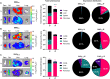
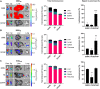
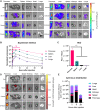
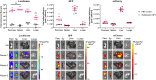
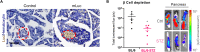
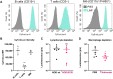
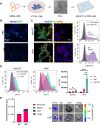
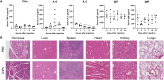
Systemic messenger RNA (mRNA) delivery to organs outside the liver, spleen, and lungs remains challenging. To overcome this issue, we hypothesized that altering nanoparticle chemistry and administration routes may enable mRNA-induced protein expression outside of the reticuloendothelial system. Here, we describe a strategy for delivering mRNA potently and specifically to the pancreas using lipid nanoparticles. Our results show that delivering lipid nanoparticles containing cationic helper lipids by intraperitoneal administration produces robust and specific protein expression in the pancreas. Most resultant protein expression occurred within insulin-producing β cells. Last, we found that pancreatic mRNA delivery was dependent on horizontal gene transfer by peritoneal macrophage exosome secretion, an underappreciated mechanism that influences the delivery of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. We anticipate that this strategy will enable gene therapies for intractable pancreatic diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- N. Pardi, M. J. Hogan, R. S. Pelc, H. Muramatsu, H. Andersen, C. R. De Maso, K. A. Dowd, L. L. Sutherland, R. M. Scearce, R. Parks, W. Wagner, A. Granados, J. Greenhouse, M. Walker, E. Willis, J.-S. Yu, C. E. McGee, G. D. Sempowski, B. L. Mui, Y. K. Tam, Y.-J. Huang, D. Vanlandingham, V. M. Holmes, H. Balachandran, S. Sahu, M. Lifton, S. Higgs, S. E. Hensley, T. D. Madden, M. J. Hope, K. Karikó, S. Santra, B. S. Graham, M. G. Lewis, T. C. Pierson, B. F. Haynes, D. Weissman, Zika virus protection by a single low-dose nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination. Nature 543, 248–251 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- M. Brazzoli, D. Magini, A. Bonci, S. Buccato, C. Giovani, R. Kratzer, V. Zurli, S. Mangiavacchi, D. Casini, L. M. Brito, E. De Gregorio, P. W. Mason, J. B. Ulmer, A. J. Geall, S. Bertholet, Induction of broad-based immunity and protective efficacy by self-amplifying mRNA vaccines encoding influenza virus hemagglutinin. J. Virol. 90, 332–344 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- M. J. Mulligan, K. E. Lyke, N. Kitchin, J. Absalon, A. Gurtman, S. Lockhart, K. Neuzil, V. Raabe, R. Bailey, K. A. Swanson, P. Li, K. Koury, W. Kalina, D. Cooper, C. Fontes-Garfias, P.-Y. Shi, Ö. Türeci, K. R. Tompkins, E. E. Walsh, R. Frenck, A. R. Falsey, P. R. Dormitzer, W. C. Gruber, U. Şahin, K. U. Jansen, Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 586, 589–593 (2020). - PubMed
-
- L. A. Jackson, E. J. Anderson, N. G. Rouphael, P. C. Roberts, M. Makhene, R. N. Coler, M. P. M. Cullough, J. D. Chappell, M. R. Denison, L. J. Stevens, A. J. Pruijssers, A. M. Dermott, B. Flach, N. A. Doria-Rose, K. S. Corbett, K. M. Morabito, S. O’Dell, S. D. Schmidt, P. A. Swanson II, M. Padilla, J. R. Mascola, K. M. Neuzil, H. Bennett, W. Sun, E. Peters, M. Makowski, J. Albert, K. Cross, W. Buchanan, R. Pikaart-Tautges, J. E. Ledgerwood, B. S. Graham, J. H. Beigel; mRNA- Study Group , An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1920–1931 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

