Speech/Language Impairment or Specific Learning Disability? Examining the Usage of Educational Categories
- PMID: 36706457
- PMCID: PMC10023181
- DOI: 10.1044/2022_JSLHR-21-00636
Speech/Language Impairment or Specific Learning Disability? Examining the Usage of Educational Categories
Abstract
Purpose: Developmental language disorder (DLD) is a lifelong condition that when impacting educational performance is identified and serviced through U.S. schools as outlined in the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act. A few examples of educational categories that refer to DLD are (a) speech or language impairment (S/LI) and (b) specific learning disability (SLD). In this research note, we aim to examine trends in how these categories are assigned.
Method: We analyzed publicly available data released by the U.S. Department of Education from six school years between 2010 and 2020. We examined the use of S/LI and SLD categories across students of different ages at the U.S. national and state levels.
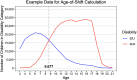
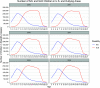
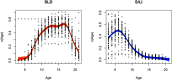
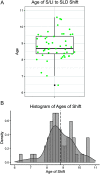
Results: We present a trend in which younger students tend to be identified with the S/LI category, whereas older students tend to be identified with the SLD category. This trend is evident in all 6 years of data analyzed at the national level, and in 49 of 50 states.
Conclusions: We discuss these findings in the context of research on language disorders to explain this trend. We highlight the potential damaging effects of using inconsistent terminology, including affecting the services for which students with DLD qualify and causing confusion for their parents and educators.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Decade of Disproportionality: A State-Level Analysis of African American Students Enrolled in the Primary Disability Category of Speech or Language Impairment.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2019 Apr 23;50(2):267-282. doi: 10.1044/2018_LSHSS-17-0149. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2019. PMID: 30973798
-
Prevalence of communication disorders compared with other learning needs in 14,500 primary and secondary school students.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2007 Mar;42 Suppl 1:37-59. doi: 10.1080/13682820601173262. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2007. PMID: 17454236
-
Effectiveness of 1:1 speech and language therapy for older children with (developmental) language disorder.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2017 Jul;52(4):528-539. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12297. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2017. PMID: 27859986
-
Putting Policy Into Practice: Impact of the Every Student Succeeds Act on Speech-Language Pathologists and Students With Disabilities.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2021 Jul 7;52(3):949-954. doi: 10.1044/2021_LSHSS-20-00139. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2021. PMID: 34139134 Review.
-
[Specific developmental disorder of speech and language in adulthood].Psychiatriki. 2012 Jun;23 Suppl 1:74-81. Psychiatriki. 2012. PMID: 22796976 Review. Greek, Modern.
Cited by
-
Caregiver Perceptions of an Asynchronous Video-Based Training on Developmental Language Disorder: A Mixed-Methods Study.Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2025 Jul 16;56(3):701-718. doi: 10.1044/2025_LSHSS-24-00091. Epub 2025 May 21. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2025. PMID: 40397786
References
-
- Adlof, S. M. , & Hogan, T. P. (2018). Understanding dyslexia in the context of developmental language disorders. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 49(4), 762–773. https://doi.org/10.1044/2018_LSHSS-DYSLC-18-0049 - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (2016). Speech-language impairments rank first, second highest by age. The ASHA Leader, 21(4), 13. https://doi.org/10.1044/leader.NIB4.21042016.13
-
- Bishop, D. V. M. (2009). Specific language impairment as a language learning disability. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 25(2), 163–165. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265659009105889
-
- Bishop, D. V. M. (2014). Ten questions about terminology for children with unexplained language problems. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 49(4), 381–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/1460-6984.12101 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop, D. V. M. , Snowling, M. J. , Thompson, P. A. , Greenhalgh, T. , & the CATALISE-2 Consortium. (2017). Phase 2 of CATALISE: A multinational and multidisciplinary Delphi consensus study of problems with language development: Terminology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(10), 1068–1080. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12721 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

