The Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib and pan-ErbB inhibitor neratinib are highly synergistic in HER2 overexpressing epithelial ovarian carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 36706643
- PMCID: PMC10023457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2023.01.015
The Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib and pan-ErbB inhibitor neratinib are highly synergistic in HER2 overexpressing epithelial ovarian carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Introduction: Ovarian cancer (OC) is associated with the highest gynecologic cancer mortality. The development of novel, effective combinations of targeted therapeutics remains an unmet medical need. We evaluated the preclinical efficacy of the Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor (olaparib) and the pan-ErbB inhibitor (neratinib) as single agents and in combination in ovarian cancer cell lines and xenografts with variable HER2 expression.
Methods: In vitro cell viability with olaparib, neratinib, and their combination was assessed using flow-cytometry based assays against a panel of OC primary cell lines with variable HER2 expression. Immunoblotting experiments were performed to elucidate the mechanism of activity and synergism. The in vivo antitumor activity of the olaparib/neratinib combination versus single agents was tested in HER2 positive xenograft OC models.
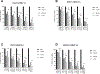
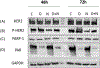
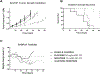
Results: HER2 + OC cell lines demonstrated higher sensitivity to olaparib and neratinib when compared to HER2 negative tumors (i.e., IC50: 2.06 ± 0.33 μM vs. 39.28 ± 30.51 μM, p = 0.0035 for olaparib and 19.42 ± 2.63 nM vs. 235.0 ± 165.0 nM, p = 0.0035 for neratinib). The combination of olaparib with neratinib was more potent when compared to single-agent olaparib or neratinib both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrated synergy in all primary HER2 + OC models. Western blot experiments showed neratinib decreased pHER2/neu while increased Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) enzymatic activity; olaparib increased pHER2/Neu expression and blocked PAR activatio. Olaparib/neratinib in combination decreased both pHER2/Neu as well as PAR activation.
Conclusion: The combination of olaparib and neratinib is synergistic and endowed with remarkable preclinical activity against HER2+ ovarian cancers. This combination may represent a novel therapeutic option for ovarian cancer patients with HER2+, homologous recombination-proficient tumors resistant to chemotherapy.
Keywords: HER2; Neratinib; Olaparib; Ovarian cancer; PARP inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. Santin declares grants from PUMA, grants from IMMUNOMEDICS, grants from GILEAD, grants from SYNTHON, grants and personal fees from MERCK, grants from BOEHINGER-INGELHEIM, grants from GENENTECH, grants and personal fees from TESARO and grants and personal fees from EISAI and R-PHARM-US. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic activity of neratinib in combination with olaparib in uterine serous carcinoma overexpressing HER2/neu.Gynecol Oncol. 2022 Aug;166(2):351-357. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2022.05.021. Epub 2022 May 28. Gynecol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35641325
-
Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) signature-3 in ovarian and uterine carcinosarcomas correlates with preclinical sensitivity to Olaparib, a poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]- ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.Gynecol Oncol. 2022 Jul;166(1):117-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2022.05.005. Epub 2022 May 20. Gynecol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35599167
-
An effective AKT inhibitor-PARP inhibitor combination therapy for recurrent ovarian cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022 May;89(5):683-695. doi: 10.1007/s00280-022-04403-9. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35419627 Free PMC article.
-
Olaparib: an oral PARP-1 and PARP-2 inhibitor with promising activity in ovarian cancer.Future Oncol. 2015;11(5):747-57. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.313. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25757679 Review.
-
Patient Counseling and Management of Symptoms During Olaparib Therapy for Recurrent Ovarian Cancer.Oncologist. 2016 Aug;21(8):954-63. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0268. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27256873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BAG2, MAD2L1, and MDK are cancer-driver genes and candidate targets for novel therapies in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Nov;31(11):1708-1720. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00805-4. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 39300217 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic advances for HER2-expressing or amplified gynecologic cancers.Gynecol Oncol. 2025 Apr;195:152-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2025.03.011. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Gynecol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40117942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Niraparib plays synergistic antitumor effects with NRT in a mouse ovarian cancer model with HRP.Transl Oncol. 2024 Nov;49:102094. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102094. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39163760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Cannistra SA. Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2519–29. - PubMed
-
- Lord CJ, Garrett MD, Ashworth A. Targeting the double-strand DNA break repair pathway as a therapeutic strategy. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4463–8. - PubMed
-
- Audeh MW, Carmichael J, Penson RT, Friedlander M, Powell B, Bell-McGuinn KM, et al. Oral poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and recurrent ovarian cancer: a proof-of-concept trial. Lancet. 2010;376:245–51. - PubMed
-
- Ledermann J, Oza AM, Lorusso D, Aghajanian C, Oaknin A, Dean A, et al. LBA40_PRARIEL3: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind study of rucaparib vs placebo following response to platinum-based chemotherapy for recurrent ovarian carcinoma (OC). Annals of Oncology. 2017;28:mdx440.034–mdx440.034.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

