Targeting Notch1-YAP Circuit Reprograms Macrophage Polarization and Alleviates Acute Liver Injury in Mice
- PMID: 36706917
- PMCID: PMC10036742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.01.002
Targeting Notch1-YAP Circuit Reprograms Macrophage Polarization and Alleviates Acute Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatic immune system disorder plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of acute liver injury. The intrinsic signaling mechanisms responsible for dampening excessive activation of liver macrophages are not completely understood. The Notch and Hippo-YAP signaling pathways have been implicated in immune homeostasis. In this study, we investigated the interactive cell signaling networks of Notch1/YAP pathway during acute liver injury.
Methods: Myeloid-specific Notch1 knockout (Notch1M-KO) mice and the floxed Notch1 (Notch1FL/FL) mice were subjected to lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine toxicity. Some mice were injected via the tail vein with bone marrow-derived macrophages transfected with lentivirus-expressing YAP. Some mice were injected with YAP siRNA using an in vivo mannose-mediated delivery system.
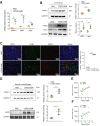
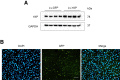
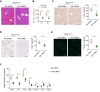
Results: We found that the activated Notch1 and YAP signaling in liver macrophages were closely related to lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury. Macrophage/neutrophil infiltration, proinflammatory mediators, and hepatocellular apoptosis were markedly ameliorated in Notch1M-KO mice. Importantly, myeloid Notch1 deficiency depressed YAP signaling and facilitated M2 macrophage polarization in the injured liver. Furthermore, YAP overexpression in Notch1M-KO livers exacerbated liver damage and shifted macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype. Mechanistically, macrophage Notch1 signaling could transcriptionally activate YAP gene expression. Reciprocally, YAP transcriptionally upregulated the Notch ligand Jagged1 gene expression and was essential for Notch1-mediated macrophage polarization. Finally, dual inhibition of Notch1 and YAP in macrophages further promoted M2 polarization and alleviated liver damage.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore a novel molecular insight into the Notch1-YAP circuit for controlling macrophage polarization in acute liver injury, raising the possibility of targeting macrophage Notch1-YAP circuit as an effective strategy for liver inflammation-related diseases.
Keywords: Acute Liver Injury; Liver Inflammation; Macrophage Polarization; Notch Signaling; YAP.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Bernal W., Lee W.M., Wendon J., et al. Acute liver failure: a curable disease by 2024? J Hepatol. 2015;62(Suppl 1):S112–S120. - PubMed
-
- Possamai L.A., Thursz M.R., Wendon J.A., et al. Modulation of monocyte/macrophage function: a therapeutic strategy in the treatment of acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014;61:439–445. - PubMed
-
- Bernal W., Auzinger G., Dhawan A., et al. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010;376:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Zhou D., Huang C., Lin Z., et al. Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2014;26:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Strnad P., Tacke F., Koch A., et al. Liver: guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:55–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

