Single-cell analysis reveals lysyl oxidase (Lox)+ fibroblast subset involved in cardiac fibrosis of diabetic mice
- PMID: 36706988
- PMCID: PMC10703720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.01.018
Single-cell analysis reveals lysyl oxidase (Lox)+ fibroblast subset involved in cardiac fibrosis of diabetic mice
Abstract
Introduction: Myocardial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction are the main characteristics of diabetic heart disease. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying diabetic myocardial fibrosis remain unclear.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the heterogeneity of cardiac fibroblasts in diabetic mice and its possible mechanism in the development of diabetic myocardial fibrosis.
Methods: We established a diabetic mouse model by injecting mice with streptozotocin. The overall cell profiles in diabetic hearts were analyzed using single-cell RNA transcriptomic techniques. Cardiac function was evaluated by echocardiography. Cardiac fibrosis was assessed by Masson's trichrome and Sirius red staining. Protein expression was analyzed using Western blotting and immunofluorescence staining.
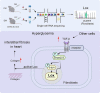
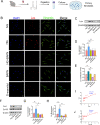
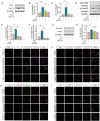
Results: A total of 11,585 cells were captured in control (Ctrl) and diabetic (DM) hearts. Twelve cell types were identified in this study. The number of fibroblasts was significantly higher in the DM hearts than in the Ctrl group. The fibroblasts were further re-clustered into nine subsets. Interestingly, cluster 4 fibroblasts were significantly increased in diabetic hearts compared with other fibroblast clusters. Lysyl oxidase (Lox) was highly expressed in DM fibroblasts (especially in cluster 4). Beta-aminopropionitrile, a Lox inhibitor, inhibited collagen expression and alleviated cardiac dysfunction in the diabetic group. Lysyl oxidase inhibition also reduced high glucose-induced collagen protein upregulation in primary fibroblasts. Moreover, a TGF-β receptor inhibitor not only prevented an increase in Lox and Col I but also inhibited the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in fibroblasts.
Conclusions: This study revealed the heterogeneity of cardiac fibroblasts in diabetic mice for the first time. Fibroblasts with high expression of Lox (cluster 4 fibroblasts) were identified to play a crucial role in fibrosis in diabetic heart disease. The findings of this study may provide a possible therapeutic target for interstitial fibrosis.
Keywords: Single-cell RNA sequencing; diabetic cardiomyopathy; fibroblasts; lysyl oxidase.
Copyright © 2023. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Induction of LOX by TGF-β1/Smad/AP-1 signaling aggravates rat myocardial fibrosis and heart failure.IUBMB Life. 2019 Nov;71(11):1729-1739. doi: 10.1002/iub.2112. Epub 2019 Jul 18. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 31317653
-
Inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 improves myocardial fibrosis and dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 1;172(1):202-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24485636
-
Upregulation of lysyl oxidase and MMPs during cardiac remodeling in human dilated cardiomyopathy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Jan;307(1-2):159-67. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9595-2. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17849172
-
Role of lysyl oxidase in myocardial fibrosis: from basic science to clinical aspects.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):H1-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00335.2010. Epub 2010 May 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20472764 Review.
-
Functions and Mechanisms of Pro-Lysyl Oxidase Processing in Cancers and Eye Pathologies with a Focus on Diabetic Retinopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 3;23(9):5088. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095088. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and Challenges in Targeting TGF-β Isoforms for Therapeutic Intervention of Cancer: A Mechanism-Based Perspective.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;17(4):533. doi: 10.3390/ph17040533. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Lysyl Oxidase-Like Protein 3 in the Pathogenesis of Graves' Orbitopathy in Orbital Fibroblasts.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Nov 4;65(13):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.13.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39546293 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β polarization in M1 macrophage mediates myocardial fibrosis in diabetes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111858. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111858. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38492336 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics and experimental validation studies reveal key biomarkers of cellular senescence in diabetic retinopathy.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Aug 12;17(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01899-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40790234 Free PMC article.
-
LOX-induced tubulointerstitial fibrosis via the TGF-β/LOX/Snail axis in diabetic mice.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 9;23(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06056-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39789539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seferović PM, Paulus WJ. Clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: a two-faced disease with restrictive and dilated phenotypes. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(27):1718-27, 27a-27c.10.1093/eurheartj/ehv134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

