Audiological outcome after stapes surgery in relation to prosthesis type
- PMID: 36707432
- PMCID: PMC10220147
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-07822-3
Audiological outcome after stapes surgery in relation to prosthesis type
Abstract
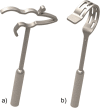
Purpose: Different techniques are used to fix crimp and CliP® Piston stapes prostheses to the long process of the incus (LPI). The CliP® Piston provides a stiff connection in contrast to the static bended loop of the crimp prosthesis, which imitates the physiological incudostapedial joint (ISJ) and thereby potentially leads to different hearing outcome.
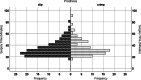
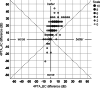
Methods: In a retrospective single-center study of German-speaking one hundred and ninety patients who underwent stapes surgery CliP® Piston or crimp prostheses between the years of 2016 and 2019 by the same surgeon and in the same setting. Pre- and postoperative bone- (BC) and air-conduction (AC) pure-tone thresholds, pre- and postoperative air-bone gap (ABG) for 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4 kHz and the surgery time were examined.
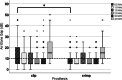
Results: The postoperative bone conduction thresholds were significantly lower in the frequencies between 0.5 and 3 kHz and the mean ABG was < 10 dB in most cases independent of the prosthesis used. Crimp prosthesis showed a significantly better closure of the ABG at 0.5 kHz.
Conclusions: The audiological outcome after stapes surgery is dependent on the type of prosthesis used, as reflected by the frequency-specific air-bone gap. The better ABG closure with the crimp prosthesis might be the result of the connection to the LPI imitating the physiological ISJ. The crimp prosthesis may be the better choice if use of hearing aids is expected postoperatively.
Keywords: Air–bone gap; Audiological outcome; Prosthesis type; Stapes surgery; Surgery time.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
First experience with a new stapes clip piston in stapedotomy.Otol Neurotol. 2005 Jul;26(4):595-8. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000178132.89353.54. Otol Neurotol. 2005. PMID: 16015152
-
Revision stapes surgery for lysis of the long process of the incus: comparing hydroxyapatite bone cement versus malleovestibulopexy and total ossicular replacement prosthesis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Sep;273(9):2515-21. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3843-y. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26690574
-
[Stapes surgery for otosclerosis using a new titanium prosthesis with a superelastic nitinol clip: First experiences].HNO. 2016 Feb;64(2):111-6. doi: 10.1007/s00106-015-0100-z. HNO. 2016. PMID: 26662464 German.
-
Endoscopic stapes surgery outcomes and complication rates: a systematic review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Aug;278(8):2673-2679. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06388-8. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33001293
-
Nitinol Prosthesis in Stapes Surgery: Evolution from Heat-Activated to Superelastic Nitinol: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 7;14(4):1069. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041069. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the coupling quality of partial prostheses at the stapes head.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May;282(5):2301-2312. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-09105-x. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39613854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shea JJ., Jr A personal history of stapedectomy. Am J Otol. 1998;19(5 Suppl):S2–12. - PubMed
-
- Toscano ML, Shermetaro C (2022) Stapedectomy. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562205/ - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

