Polymorphic Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers: Characterization and Differential Detection with Novel Corresponding Antibodies
- PMID: 36707462
- PMCID: PMC9883140
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-023-03211-3
Polymorphic Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers: Characterization and Differential Detection with Novel Corresponding Antibodies
Abstract
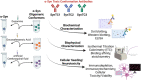
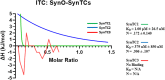
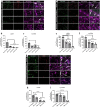
The pathological hallmark of many neurodegenerative diseases is the accumulation of characteristic proteinaceous aggregates. Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies can be characterized as synucleinopathies due to the abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein (α-Syn). Studies have shown amyloidogenic proteins such as α-Syn and tau can exist as polymorphic aggregates, a theory widely studied mostly in their fibrillar morphology. It is now well understood that an intermediate state of aggregates, oligomers, are the most toxic species. We have shown α-Syn, when modified by different physiological inducers, result in distinct oligomeric conformations of α-Syn. Polymorphic α-Syn oligomers exhibit distinct properties such as aggregate size, conformation, and differentially interact with tau. In this study, we confirm α-Syn oligomeric polymorphs furthermore using in-house novel α-Syn toxic conformation monoclonal antibodies (SynTCs). It is unclear the biological relevance of α-Syn oligomeric polymorphisms. Utilizing a combination of biochemical, biophysical, and cell-based assays, we characterize α-Syn oligomeric polymorphs. We found α-Syn oligomeric polymorphs exhibit distinct immunoreactivity and SynTCs exhibit differential selectivity and binding affinity for α-Syn species. Isothermal titration calorimetry experiments suggest distinct α-Syn:SynTC binding enthalpies in a species-specific manner. Additionally, we found SynTCs differentially reduce α-Syn oligomeric polymorph-mediated neurotoxicity and propagation in primary cortical neurons in a polymorph-specific manner. These studies demonstrate the biological significance of polymorphic α-Syn oligomers along with the importance of polymorph-specific antibodies that target toxic α-Syn aggregates. Monoclonal antibodies that can target the conformational heterogeneity of α-Syn oligomeric species and reduce their mediated toxicity have promising immunotherapeutic potential.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Amyloid; Monoclonal antibodies; Neurotoxicity; Oligomers; Protein aggregation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
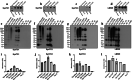
Similar articles
-
Polymorphic α-Synuclein Strains Modified by Dopamine and Docosahexaenoic Acid Interact Differentially with Tau Protein.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jun;57(6):2741-2765. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01913-6. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32350746 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of novel conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies for α-synuclein pathology.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jul;79:81-99. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25937088
-
Distinct region-specific alpha-synuclein oligomers in A53T transgenic mice: implications for neurodegeneration.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 3;30(9):3409-18. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4977-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20203200 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019 Oct;1867(10):890-908. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019. PMID: 30853581 Review.
-
Liquid-liquid Phase Separation of α-Synuclein: A New Mechanistic Insight for α-Synuclein Aggregation Associated with Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis.J Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 15;435(1):167713. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167713. Epub 2022 Jul 3. J Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 35787838 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site.Biomolecules. 2024 May 26;14(6):627. doi: 10.3390/biom14060627. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927031 Free PMC article.
-
A brain-derived tau oligomer polymorph is associated with cognitive resilience to Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Aug;21(8):e70550. doi: 10.1002/alz.70550. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40823851 Free PMC article.
-
Anionic Lipid Catalyzes the Generation of Cytotoxic Insulin Oligomers.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 11;15(7):994. doi: 10.3390/biom15070994. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723866 Free PMC article.
-
Anionic lipid catalyzes the generation of cytotoxic insulin oligomers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 18:2025.01.14.633028. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.14.633028. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 11;15(7):994. doi: 10.3390/biom15070994. PMID: 39868250 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Hypothermia Shifts Neurodegeneration Phenotype in Neonatal Human Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy but Not in Related Piglet Models: Possible Relationship to Toxic Conformer and Intrinsically Disordered Prion-like Protein Accumulation.Cells. 2025 Apr 12;14(8):586. doi: 10.3390/cells14080586. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277911 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

