The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer
- PMID: 36707507
- PMCID: PMC9883452
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer
Abstract
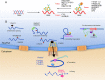
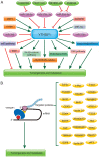
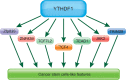
m6A is an important RNA methylation in progression of various human cancers. As the m6A reader protein, YTHDF1 is reported to accelerate m6A-modified mRNAs translation in cytoplasm. It is highly expressed in various human cancers and contributes to the progression and metastasis of cancers. YTHDF1 was closely associated with poor prognosis and also used as a molecular marker for clinical diagnosis or therapy in human cancers. It has been reported to promote chemoresistance to Adriamycin, Cisplatin and Olaparib by increasing mRNA stability of its target molecule. Moreover, it contributes to CSC-like characteristic of tumor cells and inducing the antitumor immune microenvironment. Here, we reviewed the clinical diagnostic and prognostic values of YTHDF1, as well as the molecular mechanisms of YTHDF1 in progression and metastasis of human cancers.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3816-3831. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa048. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31996915 Free PMC article.
-
ELK1-mediated YTHDF1 drives prostate cancer progression by facilitating the translation of Polo-like kinase 1 in an m6A dependent manner.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;18(16):6145-6162. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75063. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36439881 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer progression by facilitating FOXM1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner.Cell Biosci. 2022 Feb 23;12(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00759-w. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35197112 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor biology and human diseases.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 4;26:1270-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.023. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34853726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA-Binding Protein YTHDF1 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Function, Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Implication.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;14(14):3489. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143489. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA N6-Methyladenosine-Binding Protein YTHDFs Redundantly Attenuate Cancer Immunity by Downregulating IFN-γ Signaling in Gastric Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(3):e2410806. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410806. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39587835 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-YTHDF1 Mediated Regulation of GRIN2D in Bladder Cancer Progression and Aerobic Glycolysis.Biochem Genet. 2025 Aug;63(4):3220-3239. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10875-6. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38951355
-
Epigenetics of Conjunctival Melanoma: Current Knowledge and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 31;16(21):3687. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213687. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A RNA methylation: a pivotal regulator of tumor immunity and a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 28;23(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06221-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40022120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence: from homeostasis to pathological implications and therapeutic strategies.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 3;16:1534263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1534263. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39963130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paramasivam A, Priyadharsini JV. m6A RNA methylation in heart development, regeneration and disease. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:1236–37. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

