Manipulation of sterol homeostasis for the production of 24-epi-ergosterol in industrial yeast
- PMID: 36707526
- PMCID: PMC9883489
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36007-z
Manipulation of sterol homeostasis for the production of 24-epi-ergosterol in industrial yeast
Abstract
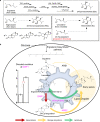
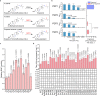
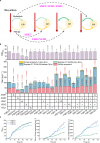
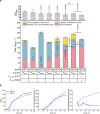
Brassinolide (BL) is the most biologically active compound among natural brassinosteroids. However, the agricultural applications are limited by the extremely low natural abundance and the scarcity of synthetic precursors. Here, we employ synthetic biology to construct a yeast cell factory for scalable production of 24-epi-ergosterol, an un-natural sterol, proposed as a precursor for BL semi-synthesis. First, we construct an artificial pathway by introducing a Δ24(28) sterol reductase from plants (DWF1), followed by enzyme directed evolution, to enable de novo biosynthesis of 24-epi-ergosterol in yeast. Subsequently, we manipulate the sterol homeostasis (overexpression of ARE2, YEH1, and YEH2 with intact ARE1), maintaining a balance between sterol acylation and sterol ester hydrolysis, for the production of 24-epi-ergosterol, whose titer reaches to 2.76 g L-1 using fed-batch fermentation. The sterol homeostasis engineering strategy can be applicable for bulk production of other economically important phytosterols.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gudesblat GE, Russinova E. Plants grow on brassinosteroids. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011;14:530–537. - PubMed
-
- Liu JN, et al. Structure-activity relationship of brassinosteroids and their agricultural practical usages. Steroids. 2017;124:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Grove MD, et al. Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica Napus pollen. Nature. 1979;281:216–217.
-
- Oklestkova J, Rarova L, Kvasnica M, Strnad M. Brassinosteroids: synthesis and biological activities. Phytochem. Rev. 2015;14:1053–1072.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

