Time-dependent microbial shifts during crayfish decomposition in freshwater and sediment under different environmental conditions
- PMID: 36707669
- PMCID: PMC9883499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28713-x
Time-dependent microbial shifts during crayfish decomposition in freshwater and sediment under different environmental conditions
Abstract
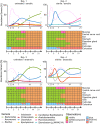
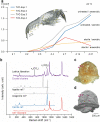
Fossilization processes and especially the role of bacterial activity during the preservation of organic material has not yet been well understood. Here, we report the results of controlled taphonomic experiments with crayfish in freshwater and sediment. 16S rRNA amplicon analyzes showed that the development of the bacterial community composition over time was correlated with different stages of decay and preservation. Three dominating genera, Aeromonas, Clostridium and Acetobacteroides were identified as the main drivers in the decomposition of crayfish in freshwater. Using micro-computed tomography (µ-CT), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and confocal Raman spectroscopy (CRS), calcite clusters were detected after 3-4 days inside crayfish carcasses during their decomposition in freshwater at 24 °C. The precipitation of calcite clusters during the decomposition process was increased in the presence of the bacterial genus Proteocatella. Consequently, Proteocatella might be one of the bacterial genera responsible for fossilization.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adipocere formation in biofilms as a first step in soft tissue preservation.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 16;12(1):10122. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14119-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35710834 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome of the Successful Freshwater Invader, the Signal Crayfish, and Its Changes along the Invasion Range.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0038921. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00389-21. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34494878 Free PMC article.
-
Sources of protein diet differentially stimulate the gut and water microbiota under freshwater crayfish, marron (Cherax cainii, Austin 2002) culture.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2022 Apr;14(2):286-298. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.13049. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35130581 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct bacterial communities in the environmental water, sediment and intestine between two crayfish-plant coculture ecosystems.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jun;105(12):5087-5101. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11369-w. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34086119
-
Sediment-associated microbial community profiling: sample pre-processing through sequential membrane filtration for 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Jan 20;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02441-0. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35057747 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A microbial flora with superior pollutant removal efficiency and its fermentation process optimization.AMB Express. 2023 Oct 17;13(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01604-0. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37848696 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen-dependent biofilm dynamics in leaf decay: an in vitro analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 20;14(1):6728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57223-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38509138 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial methods matter: Identifying discrepancies between microbiome denoising pipelines using a leaf biofilm taphonomic dataset.Appl Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 8;13(2):e11628. doi: 10.1002/aps3.11628. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Appl Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40308898 Free PMC article.
-
Composition and functional diversity of bacterial communities during swine carcass decomposition.Anim Biosci. 2023 Sep;36(9):1453-1464. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0140. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Anim Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37402447 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic phosphatization of fish scales-a pathway for fish fossilization.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 9;14(1):8347. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59025-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38594297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seilacher A. Arbeitskonzept zur konstruktions-morphologie. Lethaia. 1970;3:393–396.
-
- Seilacher BA, Reif W-E, Westphal F. Sedimentological, ecological and temporal patterns of fossil Lagerstätten. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1985;311:5–23.
-
- Singhal PK, Gaur S, Talegaonkar L. Relative contribution of different decay processes to the decomposition of Eichhornia crassipes. Aquat. Bot. 1992;42:265–272.
-
- Vass AA. Beyond the grave—Understanding human decomposition. Microbiol. Today. 2001;28:190–193.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

