Comparison of the effect of oral and vaginal misoprostol on labor induction: updating a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies
- PMID: 36707858
- PMCID: PMC9881312
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01007-8
Comparison of the effect of oral and vaginal misoprostol on labor induction: updating a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies
Abstract
Objectives: This study is aimed to compare the effect of oral misoprostol with vaginal misoprostol to induce labor as a systematic review and meta-analysis.
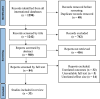
Methods: Electronic databases including PubMed [Medline], Scopus, Web of science, Embase, Ovid, Cochrane library, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched using the relevant keywords. All RCTs comparing the effect of oral vs vaginal misoprostol on labor induction were considered. The Cochrane Risk of Bias checklist was used for assessing quality of included RCTs. All statistical analyses were completed using STATA (Version 16) and Revman (Version 5).
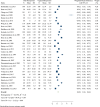
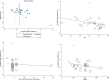
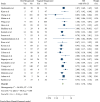
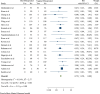
Results: Thirty-three RCTs with 5162 patients (1560 in oral and 2602 in vaginal groups) were included in this meta-analysis. Labor induction length did differ significantly between the two routes of misoprostol administration [Standardized Mean Difference: 0.40 h, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.34, 0.46; I2: 66.35%; P = 0.04]. In addition, the risk of neonatal death, tachysystole, uterine hyperstimulation, preeclampsia, non-FHR and abortion was lower in the oral misoprostol group and the risk of hypertonus, PROM, oxytocin need and cesarean fever was higher in this group than the vaginal misoprostol group.
Conclusions: Based on results of this meta-analysis, it can be inferred that currently, clinical specialists can decide to use this drug orally or vaginally on a case-by-case basis, depending on the condition of the pregnant mother and the baby.
Keywords: Labor induction; Meta-analysis; Oral misoprostol; Systematic review; Vaginal misoprostol.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of orally administered misoprostol with vaginally administered misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 May;180(5):1155-60. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70610-1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10329871 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of oral and vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone on women experiencing labor: A systematic review and updated meta-analysis of 53 randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 4;103(40):e39861. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039861. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465774 Free PMC article.
-
Oral, vaginal and sublingual misoprostol for induction of labor.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2005 Oct;91(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.07.002. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2005. PMID: 16109419 Review.
-
Titrated oral misoprostol versus static regimen of oral misoprostol for induction of labour: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022 Aug;42(6):1653-1661. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2022.2054687. Epub 2022 May 25. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022. PMID: 35611858
-
A randomized comparison of oral and intravaginal misoprostol for labor induction.Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Jun;95(6 Pt 1):905-8. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(00)00815-2. Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10831989 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of misoprostol versus oxytocin for labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes: a meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07592-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40259229 Free PMC article.
-
A disproportionality analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for misoprostol.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 19;15(1):2452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86422-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39828758 Free PMC article.
-
Factors of Non-Compliance with a Protocol for Oral Administration of Misoprostol (Angusta®) 25 Micrograms to Induce Labor: An Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 14;12(4):1521. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041521. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36836056 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Misoprostol Vaginal Inserts for Induction of Labor in Women with Very Unfavorable Cervices.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 17;12(12):4106. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124106. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cunningham FG, et al. Overview of obstetrics. Williams obstetrics. 23. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2010.
-
- Ghasemi V, et al. Effective interventions for the induction of labor: a systematic review. Iran J Obstet, Gynecol Infertil. 2018;21(1):90–104.
-
- Tan P, et al. Predictors of newborn admission after labour induction at term: Bishop score, pre-induction ultrasonography and clinical risk factors. Singapore Med J. 2008;49(3):193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

