Niche formation and function in developing tissue: studies from the Drosophila ovary
- PMID: 36707894
- PMCID: PMC9881360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-01035-7
Niche formation and function in developing tissue: studies from the Drosophila ovary
Abstract
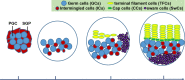
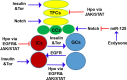
Adult stem cells have a unique ability to self-renew and to generate differentiated daughter cells that are required in the body tissues. The identity of adult stem cells is maintained by extrinsic signals from other cell types, known as niche cells. Thus, the niche is required for appropriate tissue homeostasis. Niche is formed and recruits stem cells during tissue development; therefore, it is essential to establish niche cells and stem cells in proper numbers during development. A small niche may recruit too few stem cells and cause tissue degeneration, while a large niche may maintain too many stem cells and lead to tumorigenesis. Given that vertebrate tissues are not suitable for large-scale forward genetics studies, the Drosophila ovary stands out as an excellent model for studying how multiple niche cell types and germ cells (GCs) are coordinately regulated in vivo. Recent studies are beginning to reveal how various signaling molecules regulate niche formation and how niche cells non-autonomously influence GC number. In this review, we summarize the ovarian niche structure, the key signaling pathways for niche formation, and how niche cells generate extrinsic factors to control GC proliferation during ovarian development. Video abstract.
Keywords: Drosophila; Hippo; Insulin; Niche; Ovary.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular control of the female germline stem cell niche size in Drosophila.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(21):4309-4317. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03223-0. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31300869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin and Target of rapamycin signaling orchestrate the development of ovarian niche-stem cell units in Drosophila.Development. 2013 Oct;140(20):4145-54. doi: 10.1242/dev.093773. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Development. 2013. PMID: 24026119
-
Self-maintained escort cells form a germline stem cell differentiation niche.Development. 2011 Dec;138(23):5087-97. doi: 10.1242/dev.067850. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Development. 2011. PMID: 22031542 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila ovary: an active stem cell community.Cell Res. 2007 Jan;17(1):15-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310123. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17199109 Review.
-
The Hippo pathway regulates homeostatic growth of stem cell niche precursors in the Drosophila ovary.PLoS Genet. 2015 Feb 2;11(2):e1004962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004962. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25643260 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Germline expression of Imp-L2 in Drosophila females enhances reproductive activity and longevity.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025 Mar 17;29(1):31-40. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2025.2480150. eCollection 2025. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 40103616 Free PMC article.
-
PIWI proteins and piRNAs: key regulators of stem cell biology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 6;13:1540313. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1540313. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39981094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arwert EN, Hoste E, Watt FM. Epithelial stem cells, wound healing and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:170–180. - PubMed
-
- Spradling AC, Nystul T, Lighthouse D, Morris L, Fox D, Cox R, Tootle T, Frederick R, Skora A. Stem cells and their niches: integrated units that maintain Drosophila tissues. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Schofeld R. The relationship between the spleen colony forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4:7–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

