LncRNA DICER1-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway through sponging miR-650
- PMID: 36708020
- PMCID: PMC10134332
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5550
LncRNA DICER1-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway through sponging miR-650
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a disease with high morbidity and mortality rates globally. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a fundamental role in tumor progression, and increasing attention has been paid to their role in CRC. This study aimed to determine the function of lncRNA DICER1 antisense RNA 1 (DICER1-AS1) in CRC and confirm its potential regulatory mechanisms in CRC.
Methods: The publicly available dataset was used to assess DICER1-AS1 function and expression in CRC. RT-qPCR or western blot assays were performed to verify DICER1-AS1, miR-650, and mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) expression in CRC cells or tissues. To determine the function of DICER1-AS1, we performed CCK-8, colony formation, transwell, cell cycle, and in vivo animal assays. Using RNA sequence analysis, luciferase reporter assays, and bioinformatics analysis, the connection between DICER1-AS1, MAPK1, and miR-650 was investigated.
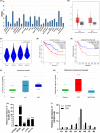
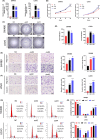
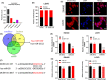
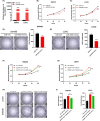
Results: DICER1-AS1 was significantly upregulated in CRC tissue compared to normal colon tissue. High DICER1-AS1 expression suggested a poor prognosis in CRC patients. Functionally, upregulation of DICER1-AS1 effectively promoted CRC proliferation, migration, and invasion ex vivo and tumor progression in vivo. Mechanistically, DICER1-AS1 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) that sponges miR-650 to upregulate MAPK1, promotes ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and sequentially activates the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our investigations found that upregulation of DICER1-AS1 activates the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway by sponging miR-650 to promote CRC progression, revealing a possible clinically significant biomarker and therapeutic target.
Keywords: DICER1-AS1; MAPK/ERK pathway; MAPK1; colorectal cancer; malignant proliferation; miR-650.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFα.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):145-156. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181503. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30010111
-
LncRNA TTN-AS1 sponges miR-376a-3p to promote colorectal cancer progression via upregulating KLF15.Life Sci. 2020 Mar 1;244:116936. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116936. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31610194
-
The miR-106b/NR2F2-AS1/PLEKHO2 Axis Regulates Migration and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer through the MAPK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 30;22(11):5877. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115877. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070923 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Key Signaling Pathways and ncRNAs in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 21;25(8):4548. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084548. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding TP73-AS1: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 20;26(8):3886. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083886. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non‑coding RNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Aug 8;28(4):486. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14619. eCollection 2024 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39185489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orientin Reduces the Effects of Repeated Procedural Neonatal Pain in Adulthood: Network Pharmacology Analysis, Molecular Docking Analysis, and Experimental Validation.Pain Res Manag. 2023 Nov 24;2023:8893932. doi: 10.1155/2023/8893932. eCollection 2023. Pain Res Manag. 2023. PMID: 38047157 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of lncRNA and mRNA differentially expressed in patients with cervical cancer.Front Bioinform. 2025 Aug 1;5:1605681. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2025.1605681. eCollection 2025. Front Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40822023 Free PMC article.
-
The macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 1 receptor plays a major role in mediating colitis-associated colorectal cancer malignancy.Immunol Cell Biol. 2025 May;103(5):444-460. doi: 10.1111/imcb.70011. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Immunol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40033767 Free PMC article.
-
The functions and mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 4;14:1419972. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1419972. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39026978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66(4):683‐691. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7‐33. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy RD, Bylesjo M, Kerr P, et al. Development and independent validation of a prognostic assay for stage II colon cancer using formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded tissue. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(35):4620‐4626. - PubMed
-
- Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non‐coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(3):155‐159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

