L1CAM promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation by miR-143-3p-induced expression of hexokinase 2 in glioma
- PMID: 36708044
- PMCID: PMC10061292
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13384
L1CAM promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation by miR-143-3p-induced expression of hexokinase 2 in glioma
Abstract
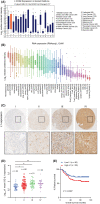
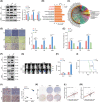
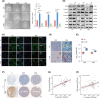
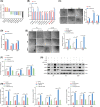
In recent decades, antiangiogenic therapy, which blocks the supply of oxygen and nutrition to tumor cells, has become a promising clinical strategy for the treatment of patients with tumors. However, recent studies revealed that vasculogenic mimicry (VM), which is the process by which vascular morphological structures are formed by highly invasive tumor cells, has been considered a potential factor for the failure of antiangiogenic therapy in patients with tumors. Thus, inhibition of VM formation might be a potential target for improving the outcome of antiangiogenic strategies. However, the mechanism underlying VM formation is still incompletely elucidated. Herein, we report that L1CAM might be a critical regulator of VM formation in glioma, and might be associated with the resistance of glioma to antiangiogenic therapy. We found that the tumor-invasion and tube-formation capabilities of L1CAM-overexpressing cells were significantly enhanced in vitro and in vivo. In addition, the results indicated that miR-143-3p, which might directly target the 3'UTR of the hexokinase 2 (HK2) gene to regulate its protein expression, was subsequently involved in L1CAM-mediated VM formation by glioma cells. Further study revealed that the regulation of MMP2, MMP9, and VEGFA expression was involved in this process. Moreover, we identified that activation of the downstream PI3K/AKT signaling pathway of the L1CAM/HK2 cascade is critical for VM formation by glioma cells. Furthermore, we found that the combined treatment of anti-L1CAM neutralizing monoclonal antibody and bevacizumab increases efficacy beyond that of bevacizumab alone, and suppresses glioma growth in vivo, indicating that the inhibition of L1CAM-mediated VM formation might efficiently improve the effect of antiangiogenic treatment for glioma patients. Together, our findings demonstrated a critical role of L1CAM in regulating VM formation in glioma, and that L1CAM might be a potential target for ameliorating tumor resistance to antiangiogenic therapy in glioma patients.
Keywords: HK2; L1CAM; glioma; miR-143-3p; vasculogenic mimicry.
© 2023 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autophagy-induced KDR/VEGFR-2 activation promotes the formation of vasculogenic mimicry by glioma stem cells.Autophagy. 2017 Sep 2;13(9):1528-1542. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1336277. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28812437 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29a-3p delivery via exosomes derived from engineered human mesenchymal stem cells exerts tumour suppressive effects by inhibiting migration and vasculogenic mimicry in glioma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 1;13(4):5055-5068. doi: 10.18632/aging.202424. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33535172 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPD interacts with ZHX2 regulating the vasculogenic mimicry formation of glioma cells via linc00707/miR-651-3p/SP2 axis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 4;12(2):153. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03432-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33542193 Free PMC article.
-
Vasculogenic mimicry in carcinogenesis and clinical applications.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Mar 14;13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00858-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32169087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and Prospects of Vasculogenic Mimicry in Glioma: A Potential New Therapeutic Target?Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 21;13:4473-4483. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S247855. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32547078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting endothelial glycolytic reprogramming by tsRNA-1599 for ocular anti-angiogenesis therapy.Theranostics. 2024 Jun 1;14(9):3509-3525. doi: 10.7150/thno.96946. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38948065 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing breast cancer Ki-67 diagnosis: ultrasound radiomics and fully connected neural networks (FCNN) combination method.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Sep;207(2):453-468. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07375-x. Epub 2024 Jun 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38853220
-
SUMOylation of RALY promotes vasculogenic mimicry in glioma cells via the FOXD1/DKK1 pathway.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):3323-3340. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09836-3. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37906341 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction Between Vasculogenic Mimicry and the Immune System: Mechanistic Insights and Dual Exploration in Cancer Therapy.Cell Prolif. 2025 Jun;58(6):e13814. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13814. Epub 2025 Jan 26. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 39865437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RCAd-LTH-shPD-L1, a double-gene recombinant oncolytic adenovirus with enhanced antitumor immunity, increases lymphocyte infiltration and reshapes the tumor microenvironment.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e007171. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007171. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38212125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY. Antiangiogenic therapies for high‐grade glioma. Nat Rev Neurol. 2009;5:610–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

