Tailoring and optimization of a honey-based nanoemulgel loaded with an itraconazole-thyme oil nanoemulsion for oral candidiasis
- PMID: 36708105
- PMCID: PMC9888461
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2173337
Tailoring and optimization of a honey-based nanoemulgel loaded with an itraconazole-thyme oil nanoemulsion for oral candidiasis
Abstract
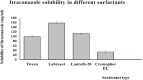
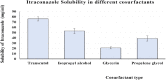
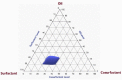
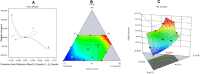
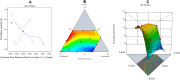
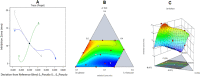
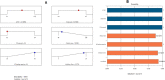
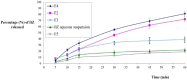
The use of essential oil-based nanoemulsions (NEs) has been the subject of extensive research on a variety of conditions affecting the oral cavity. NEs are delivery methods that improve the solubility and distribution of lipid medicines to the intended areas. Because of their antibacterial and antifungal properties, itraconazole and thyme oil-based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (ItZ-ThO-SNEDDS) were created to protect oral health against oral microorganisms. The ItZ-ThO-SNEDDS were created utilizing an extreme verices mixture design, and varying concentrations of ThO (10% and 25%), labrasol (40% and 70%), and transcutol (20% and 40%) were used. The ItZ-ThO-SNEDDS had droplet sizes of less than 250 nm, a drug-loading efficiency of up to 64%, and a fungal growth inhibition zone of up to 20 mm. The accepted design was used to obtain the ideal formulation, which contained ThO in the amount of 0.18 g/ml, labrasol 0.62 g/ml, and transcutol 0.2 g/ml. The best ItZ-ThO-SNEDDS formulation was incorporated into a honey-based gel, which demonstrated improved release of ItZ in vitro and improved transbuccal permeation ex vivo. In addition, when compared with various formulations tested in rats, the optimized loaded emulgel decreased the ulcer index. This study therefore demonstrated that the ItZ-ThO-SNEDDS could offer an effective defense against oral diseases caused by microbial infections.
Keywords: Honey-based gel; Itraconazole; Sustainability of natural resources; design of experiments; oral microbiota; thyme oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utilization of experimental design in the formulation and optimization of hyaluronic acid-based nanoemulgel loaded with a turmeric-curry leaf oil nanoemulsion for gingivitis.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2184311. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2184311. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36846914 Free PMC article.
-
Development Of Saquinavir Mesylate Nanoemulsion-Loaded Transdermal Films: Two-Step Optimization Of Permeation Parameters, Characterization, And Ex Vivo And In Vivo Evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Nov 1;14:8589-8601. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S230747. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31802871 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Coenzyme (Q10) with Improved Dissolution, Bioavailability, and Protective Efficiency on Liver Fibrosis.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Jul;18(5):1657-1672. doi: 10.1208/s12249-016-0632-x. Epub 2016 Sep 27. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 27677262
-
A Novel Nanoemulsion Intermediate Gel as a Promising Approach for Delivery of Itraconazole: Design, In Vitro and Ex Vivo Appraisal.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 Oct 6;21(7):272. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01830-w. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 33025308
-
Nanoemulsion and nanoemulgel-based carriers as advanced delivery tools for the treatment of oral diseases.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Apr;15(4):1139-1155. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01735-2. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39500820 Review.
Cited by
-
Permeability-Enhanced Liposomal Emulgel Formulation of 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Skin Cancer.Gels. 2023 Mar 9;9(3):209. doi: 10.3390/gels9030209. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36975657 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Optimization of a Novel Lozenge Containing a Metronidazole-Peppermint Oil-Tranexamic Acid Self-Nanoemulsified Delivery System to Be Used after Dental Extraction: In Vitro Evaluation and In Vivo Appraisal.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 19;15(9):2342. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092342. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765310 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Characterization of New Miconazole-Based Microemulsions for Buccal Delivery by Implementing a Full Factorial Design Modeling.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 14;16(2):271. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020271. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399325 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Encapsulating Bioactive Irish Honey into Pluronic-Based Thermoresponsive Hydrogels and Potential Application in Soft Tissue Regeneration.Gels. 2025 Mar 19;11(3):215. doi: 10.3390/gels11030215. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40136920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alhakamy NA, Hosny KM, Aldryhim AY, et al. (2022). Development and optimization of ofloxacin as solid lipid nanoparticles for enhancement of its ocular activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 72:1.
-
- Ali SA, Sindi AM, Mair YH, et al. (2021). Oral gel loaded by ethotransfersomes of antifungal drug for oral thrush: preparation, characterization, and assessment of antifungal activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 66:102841.
-
- Ali SA, Sindi AM, Mair YH, Khallaf RA. (2021). Oral gel loaded by ethotransfersomes of antifungal drug for oral thrush: preparation, characterization, and assessment of antifungal activity. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 66:102841.
-
- Alkhalidi HM, Naguib GH, Kurakula M, et al. (2018). In vitro and preclinical assessment of factorial design based nanoethosomal transdermal film formulation of mefenamic acid to overcome barriers to its use in relieving pain and inflammation. J Drug Del Sci Technol 48:450–12.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
