Lappaol F regulates the cell cycle by activating CDKN1C/p57 in human colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 36708218
- PMCID: PMC9888477
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2172048
Lappaol F regulates the cell cycle by activating CDKN1C/p57 in human colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
Context: Lappaol F (LAF), a natural lignan from Arctium lappa Linné (Asteraceae), inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. The underlying mechanism involves the suppression of the Yes-associated protein. However, the specific role of LAF in cell cycle regulation remains unknown.
Objective: This study determined the molecular mechanism by which LAF regulates cell cycle progression.
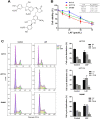
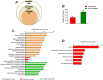
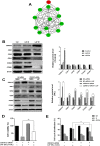
Materials and methods: Various colon cancer cell lines (SW480, HCT15, and HCT116) were treated with LAF (25, 50, and 75 μmol/L) for 48 h. The effects of LAF on cell proliferation and cell cycle were determined using sulforhodamine B and flow cytometry assays. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were identified using quantitative proteomics. Bioinformatic analysis of DEPs was conducted via Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. Expression levels of DEPs in the cell cycle pathway were analyzed using RT-qPCR and western blotting.
Results: LAF suppressed the proliferation of SW480, HCT15, and HCT116 cells (IC50 47.1, 51.4, and 32.8 μmol/L, respectively) and induced cell cycle arrest at the S phase. A total of 6331 proteins were identified and quantified, of which 127 were differentially expressed between the LAF-treated and untreated groups. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses revealed that DEPs mainly participated in the cell cycle. CDKN1C/p57 showed the most significant differential expression, with the highest fold-change (3.155-fold). Knockdown of CDKN1C/p57 attenuated the S phase cell cycle arrest and proliferation inhibition induced by LAF.
Conclusion: LAF exerts antitumor effects via S phase arrest by activating CDKN1C/p57 in colorectal cancer cells.
Keywords: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C/p57; cyclin; cyclin-dependent kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lappaol F, an anticancer agent, inhibits YAP via transcriptional and post-translational regulation.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):619-628. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1923759. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34010589 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-221 inhibits CDKN1C/p57 expression in human colorectal carcinoma.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Mar;32(3):375-84. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.206. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21278784 Free PMC article.
-
[MicroRNA-221 controls CDKN1C/P57 expression in human colorectal carcinoma].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;14(4):279-83. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21538272 Chinese.
-
The hallmarks of CDKN1C (p57, KIP2) in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1816(1):50-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21447370 Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Control of CDKN1C Expression: Importance in Cell Commitment and Differentiation, Tissue Homeostasis and Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 2;19(4):1055. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041055. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29614816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in Clinicopathological Features, P16Ink4a and P57KIP2 Immunohistochemical Expressions, and Survival Between Colorectal Carcinoma in Rectosigmoid and Other Colonic Locations.Cureus. 2024 Jun 10;16(6):e62061. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62061. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38989391 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Mechanism of Tibetan Medicine Liuwei Muxiang Pills against Colorectal Cancer: Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Analyses.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;17(4):429. doi: 10.3390/ph17040429. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675391 Free PMC article.
-
SSR markers development and their application in genetic diversity of burdock (Arctium lappa L.) germplasm.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 14;25(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06203-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39953403 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of Arctium lappa root: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic applications.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00466-8. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 39162715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-TNBC effects of Lappaol F by targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulation of GSK-3β/YAP/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 7;16:1496511. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1496511. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39989901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borriello A, Caldarelli I, Bencivenga D, Criscuolo M, Cucciolla V, Tramontano A, Oliva A, Perrotta S, Della Ragione F.. 2011. p57(Kip2) and cancer: time for a critical appraisal. Mol Cancer Res. 9(10):1269–1284. - PubMed
-
- Fotedar A, Cannella D, Fitzgerald P, Rousselle T, Gupta S, Doree M, Fotedar R.. 1996. Role for cyclin A-dependent kinase in DNA replication in human S phase cell extracts. J Biol Chem. 271(49):31627–31637. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
