Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists are monoamine oxidase-A selective inhibitors
- PMID: 36708234
- PMCID: PMC10952593
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16741
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists are monoamine oxidase-A selective inhibitors
Abstract
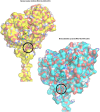
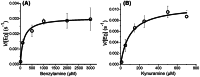
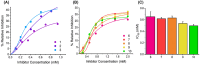
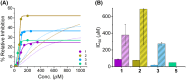
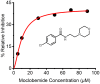
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) are one of the fastest growing classes of recreational drugs. Despite their growth in use, their vast chemical diversity and rapidly changing landscape of structures make understanding their effects challenging. In particular, the side effects for SCRA use are extremely diverse, but notably include severe outcomes such as cardiac arrest. These side effects appear at odds with the main putative mode of action, as full agonists of cannabinoid receptors. We have hypothesized that SCRAs may act as MAO inhibitors, owing to their structural similarity to known monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI's) as well as matching clinical outcomes (hypertensive crisis) of 'monoaminergic toxicity' for users of MAOIs and some SCRA use. We have studied the potential for SCRA-mediated inhibition of MAO-A and MAO-B via a range of SCRAs used commonly in the UK, as well as structural analogues to prove the atomistic determinants of inhibition. By combining in silico and experimental kinetic studies we demonstrate that SCRAs are MAO-A-specific inhibitors and their affinity can vary significantly between SCRAs, most notably affected by the nature of the SCRA 'head' group. Our data allow us to posit a putative mechanism of inhibition. Crucially our data demonstrate that SCRA activity is not limited to just cannabinoid receptor agonism and that alternative interactions might account for some of the diversity of the observed side effects and that these effects can be SCRA-specific.
Keywords: MAO-A; MAO-B; SCRAs; enzyme inhibition; flexible docking analysis; monoamine oxidase; synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists.
© 2023 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

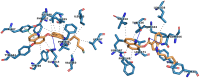

References
-
- Gunderson EW, Haughey HM, Ait‐Daoud N, Joshi AS & Hart CL (2012) “spice” and “K2” herbal highs: a case series and systematic review of the clinical effects and biopsychosocial implications of synthetic cannabinoid use in humans. Am J Addict 21, 320–326. - PubMed
-
- Banister S, Kevin R, Martin L, Adams A, MacDonald C, Manning JJ, Boyd R, Cunningham M, Stevens MY, McGregor IS et al. (2019) The chemistry and pharmacology of putative synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist (SCRA) new psychoactive substances (NPS) 5F‐PY‐PICA, 5F‐PY‐PINACA, and their analogs. Drug Test Anal 11, 976–989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

