Antiangiogenic Activity of n-hexane Insoluble Fraction and Its Tylophorine Component from Ficus septica Leaves in Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane Induced by bFGF
- PMID: 36708554
- PMCID: PMC10152866
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.1.75
Antiangiogenic Activity of n-hexane Insoluble Fraction and Its Tylophorine Component from Ficus septica Leaves in Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane Induced by bFGF
Abstract
Objective: Ficus septica is an Indonesian medicinal plant traditionally used to treat various illness, including cancer. The n-hexane insoluble fraction of the ethanolic extract of F. septica leaves (HIFFS) shows a potential anticancer activity against breast cancer cell line T47D. Considering that angiogenesis is a pivotal factor in malignant cancer growth, progression, and invasion, we aimed to investigate the antiangiogenic effect of HIFFS on chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) induced by bFGF. We also evaluated tylophorine, the cytotoxic alkaloid of F. septica.
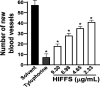
Methods: Chicken CAM was used to assess the antiangiogenic effect. Fertilized chicken eggs were induced with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) ex ovo. Prior to bFGF induction, HIFFS (2.33, 4.65, 6.98, and 9.30 μg/mL) or tylophorine (9.20 µM) was added (10 µL) to a paper disk and implanted to the CAM. After 48 h of incubation, each treatment group was photographed, and the number of new blood vessel was calculated and compared with that in the solvent-treated group to determine the antiangiogenic activity. Histology of the CAM was evaluated after hematoxylin-eosin and Mallory acid fuchsin staining.
Results: We found that HIFFS at low concentrations (2.33, 4.65, 6.98, and 9.30 μg/mL) inhibited angiogenesis activity (31.87, 41.99, 53.65, and 70.08, respectively) in chicken CAM induced by bFGF. Tylophorine (9.20 µM) also showed similar antiangiogenesis activity in the same model. Histopathology analysis revealed that HIFFS and tylophorine reduced the number of new blood vessels in CAM induced by bFGF.
Conclusion: HIFFS and tylophorine showed antiangiogenic effect on chicken CAM induced by bFGF. This finding emphasized the potential of F. septica as a candidate anticancer agent.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Anticancer; CAM; alkaloid; histopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Eelen G, Treps L, Li X, et al. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis updated. Circ Res. 2020;127:310–29. - PubMed
-
- Fallah A, Sadeghinia A, Kahroba H, et al. Therapeutic targeting of angiogenesis molecular pathways in angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:775–85. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Mahmood T, et al. Plant-derived anticancer agents: A green anticancer approach. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2017;7:1129–50.

