Efficacy and Safety of Vernonia cinerea for Smoking Cessation: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36708558
- PMCID: PMC10152872
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.1.101
Efficacy and Safety of Vernonia cinerea for Smoking Cessation: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
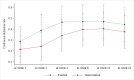
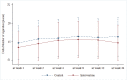
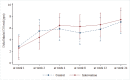
This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of Vernonia cinerea (VC) and nortriptyline for smoking cessation. A randomized, active-comparator, open-label trial was conducted in 2019. A total of 84 patients participated in the study, and equally randomized with 42 participants in each group. Overall, there was no statistically significant difference of continuous abstinence rate (CAR) between VC and nortriptyline group (Odd ratio 0.68, 95%CI 0.25-1.85, P=0.451). After week 12, the end of treatment, CAR between both groups was not different (44.44% vs 45.95%, Odd ratio 0.77, 95%CI 0.23-2.54, P>0.999). After follow up by the end of research at week 24, the CAR in both groups was not different (41.67% vs 43.24%, Odd ratio 0.76, 95%CI 0.23-2.55, P>0.999). After week 24, relapse rate between VC and nortriptyline group was not different (13.89% vs 10.81%, P=0.923). In addition, both groups were effective in reducing the number of cigarettes per day compared to baseline. However, there was no difference between the groups. Overall, the VC group had an 8% smoking rate less than nortriptyline group, but not statistically significant (IRR 0.92, 95%CI 0.59-1.43, P=0.702). They also resulted in reducing the exhaled CO level at treatment period and wash out period (at week 12; 7(-17-20) vs 7(-12-16), mean difference 0.78, 95%CI -3.07-4.63, P>0.999, at week 24; 8(-5-22) vs 8.5(-5-17), mean difference 0.39, 95%CI -3.46-4.24, P>0.999). Overall, there was no difference between either group (mean difference -0.31, 95%CI -3.10-2.47). For safety data, adverse events including tongue bitter taste or numbness were found in VC group to be greater than in nortriptyline group (61.9% vs 30.95%, P=0.004), whereas dry mouth and drowsiness were greater found in nortriptyline group (35.71% vs 90.48%, P<0.001 and 16.67% vs 90.48%, P<0.001, respectively). Serious adverse events were not found. In smoking cessation, efficacy and safety of either VC or nortriptyline showed no difference.
Keywords: Vernonia cinerea; nortriptyline; safety; smoking cessation; tobacco dependence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of cytisine versus nortriptyline for smoking cessation: A multicentre, randomized, double-blinded and placebo-controlled trial.Respirology. 2024 Oct;29(10):880-887. doi: 10.1111/resp.14787. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Respirology. 2024. PMID: 39004954 Clinical Trial.
-
Vernonia cinerea pastilles is effective for smoking cessation.J Tradit Complement Med. 2019 Oct 15;11(2):90-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.09.006. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2019. PMID: 33728267 Free PMC article.
-
A controlled trial of nortriptyline, sustained-release bupropion and placebo for smoking cessation: preliminary results.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006;19(3):205-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.05.003. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16517193 Clinical Trial.
-
Nortriptyline for smoking cessation: a review.Nicotine Tob Res. 2005 Aug;7(4):491-9. doi: 10.1080/14622200500185298. Nicotine Tob Res. 2005. PMID: 16085520 Review.
-
Varenicline: a first-line treatment option for smoking cessation.Clin Ther. 2009 Mar;31(3):463-91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.03.021. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19393839 Review.
References
-
- Chaikoolvatana A, Ayuthaya ND, Suthipinittharm P, et al. Development and evaluation of the effectiveness of Vernonia cinerea (VC) cookies for smoking cessation. Tob Prev Cessation. 2017;3:45.
-
- Chaikoolvatana A, Sithibutra C, Chandee S, Chaikoolvatana C. A comparison of Smoking Cessation Drug Therapies Related Quality of Life between Vernonia cinerea Tea and 0. 5% Sodium Nitrate Mouthwash. Nurs J. 2015;42:178–92.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical