Bacterial droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq reveals antibiotic-associated heterogeneous cellular states
- PMID: 36708705
- PMCID: PMC10014032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.002
Bacterial droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq reveals antibiotic-associated heterogeneous cellular states
Abstract
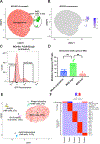
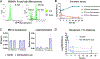
We introduce BacDrop, a highly scalable technology for bacterial single-cell RNA sequencing that has overcome many challenges hindering the development of scRNA-seq in bacteria. BacDrop can be applied to thousands to millions of cells from both gram-negative and gram-positive species. It features universal ribosomal RNA depletion and combinatorial barcodes that enable multiplexing and massively parallel sequencing. We applied BacDrop to study Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates and to elucidate their heterogeneous responses to antibiotic stress. In an unperturbed population presumed to be homogeneous, we found within-population heterogeneity largely driven by the expression of mobile genetic elements that promote the evolution of antibiotic resistance. Under antibiotic perturbation, BacDrop revealed transcriptionally distinct subpopulations associated with different phenotypic outcomes including antibiotic persistence. BacDrop thus can capture cellular states that cannot be detected by bulk RNA-seq, which will unlock new microbiological insights into bacterial responses to perturbations and larger bacterial communities such as the microbiome.
Keywords: antibiotic persistence; antibiotic perturbation; antibiotic resistance; bacterial heterogeneity; bacterial single-cell RNA-seq; droplet; massively parallel sequencing.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.T.H., P.M., and H.M.A. have filed an U.S. Patent Application (application no. 17/819,034) based on this work.
Figures
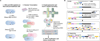



Comment in
-
Advancing massive transcriptional profiling of single bacteria.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Feb 28;3(2):100416. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100416. eCollection 2023 Feb 27. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 36936081 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

