Pre-operative anemia and peri-operative transfusion are associated with poor oncologic outcomes in cancers of the esophagus: potential impact of patient blood management on cancer outcomes
- PMID: 36709278
- PMCID: PMC9883921
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-10579-x
Pre-operative anemia and peri-operative transfusion are associated with poor oncologic outcomes in cancers of the esophagus: potential impact of patient blood management on cancer outcomes
Abstract
Background: Both Red Blood Cell (RBC) transfusion and anemia are thought to negatively impact cancer survival. These effects have been reported with mixed findings in cancer of the esophagus. The potential impact of the application of restrictive transfusion strategies on this patient population has not been defined.
Materials and methods: We conducted a retrospective study of esophagectomies and studied cases based on whether they were anemic or were transfused peri-operatively. Clinical characteristics and known clinicopathologic prognosticators were compared between these groups. Survival was compared by Cox proportional hazard modeling. Post-operative transfusions were assessed for compliance with restrictive transfusion thresholds.
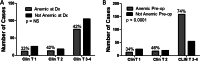
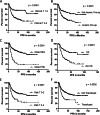
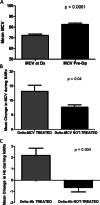
Results: Three-hundred ninety-nine esophagectomy cases were reviewed and after exclusions 348 cases were analyzed. The median length of follow-up was 33 months (range 1-152 months). Sixty-four percent of patients were anemic pre-operatively and 22% were transfused. Transfusion and anemia were closely related to each other. Microcytic anemia was uncommon but was evaluated and treated in only 50% of cases. Most anemic patients had normocytic RBC parameters. Transfusion but not anemia was associated with a protracted/prolonged post-operative stay. Transfusion and anemia were both associated with reduced survival however only anemia was associated with decreased survival in multi-variable modeling. Sixty-eight percent of patients were transfused post-operatively and 11% were compliant with the restrictive threshold of 7 g/dL.
Conclusions: Pre-operative anemia and transfusion are closely associated, however only anemia was found to compromise survival in our esophageal cancer cohort, supporting the need for more aggressive evaluation and treatment of anemia. Adherence to restrictive transfusion guidelines offers an opportunity to reduce transfusion rates which may also improve short-term outcomes.
Keywords: Anemia; Esophagectomy; Patient blood management; Transfusion.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to report.
Figures

References
-
- Blajchman MA, Dzik S, Vamvakas EC, Sweeney J, Snyder EL. Clinical and molecular basis of transfusion-induced immunomodulation: summary of the proceedings of a state-of-the-art conference. Transfus Med Rev. 2001;15(2):108–135. - PubMed
-
- Roelen DL, van Rood JJ, Brand A, Claas FH. Immunomodulation by blood transfusions. Vox Sang. 2000;78(Suppl 2):273–275. - PubMed
-
- Rouger P. Transfusion induced immunomodulation: myth or reality? Transfus Clinique et biologique : journal de la Societe francaise de transfusion sanguine. 2004;11(3):115–116. - PubMed
-
- Uchida H, Tanaka H, Kitoh Y, Yanagisawa K, To H, Tago K, Mizuta K, Fujimura A, Tominaga S, Hashizume K, et al. Mechanisms of immunomodulation induced by blood transfusion: identification of humoral factors. Transpl Proc. 2000;32(2):255–256. - PubMed
-
- Vamvakas EC, Blajchman MA. Deleterious clinical effects of transfusion-associated immunomodulation: fact or fiction? Blood. 2001;97(5):1180–1195. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

