Coronary artery disease in a patient with Addison's disease: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 36709280
- PMCID: PMC9884407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03079-0
Coronary artery disease in a patient with Addison's disease: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Addison's disease which is due to dysfunction of the adrenal gland, with abnormal secretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, is rare. By inducing inflammation and disorders of water and electrolyte metabolism, Addison's disease may accelerate progression of co-existed cardiovascular diseases. Addison's disease combined with cardiovascular disease is infrequent, only 10 cases in the literature.
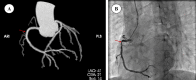
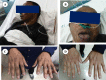
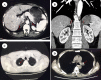
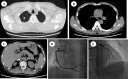
Case presentation: We reported a 51-year-old male patient with unstable angina pectoris and hypotension. Changes on coronary angiography within 2 years suggested rapid progression of coronary artery disease in a patient with low cardiovascular risk. An additional clue of skin hyperpigmentation, fatigue and further examination confirmed the diagnosis of Addison's disease caused by adrenal tuberculosis. After hormone replacement treatment, the frequency and severity of the angina pectoris were alleviated significantly, as were hypotension, hyperpigmentation and fatigue.
Conclusions: The combination of Addison's disease and coronary artery disease in one patient is rare. Addison's disease can induce inflammation and disorders of water and electrolyte metabolism, which may further accelerate the course of coronary artery disease. Meanwhile, the hypotension in Addison's disease may affect the coronary blood flow, which may result in an increased susceptibility to unstable angina in the presence of coronary stenosis. So, we should analyze comprehensively if the coronary artery disease progress rapidly.
Keywords: Addison’s disease; Adrenal tuberculosis; Case report; Coronary artery disease; Unstable angina.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author’s decalared that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subjective health status in Norwegian patients with Addison's disease.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002 May;56(5):581-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2002.01466.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002. PMID: 12030907
-
Addison's disease presenting with marked eosinophilia and psychosis.Trop Geogr Med. 1988 Jul;40(3):241-3. Trop Geogr Med. 1988. PMID: 3188216
-
Addison's disease, diffuse skin, and mucosal hyperpigmenation with subtle "flu-like" symptoms--a report of two cases.Pediatr Dermatol. 2008 Mar-Apr;25(2):215-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00637.x. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18429783
-
Addison's disease without hyperpigmentation in pediatrics: pointing towards specific causes.Hormones (Athens). 2023 Mar;22(1):143-148. doi: 10.1007/s42000-022-00415-5. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Hormones (Athens). 2023. PMID: 36348260 Review.
-
Addison's disease in pregnancy: Case report, management, and review of the literature.J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2020;13(2):275-278. doi: 10.3233/NPM-190231. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2020. PMID: 31744021 Review.
Cited by
-
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with free wall rupture and ventricular septal defect: a case report.Future Cardiol. 2024;20(10):543-546. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2024.2382541. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Future Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39101463 Free PMC article.
-
Response to the Letter to the Editor: Rare Endocrine Disorders and Peripheral Arterial Disease.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2025;23(1):9-11. doi: 10.2174/0115701611372375241125111238. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39633519 No abstract available.
-
Outcomes of ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Adrenal Insufficiency.J Endocr Soc. 2024 Oct 25;8(12):bvae186. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae186. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 39569135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Husebye ES, Allolio B, Arlt W, Badenhoop K, Bensing S, Betterle C, Falorni A, Gan EH, Hulting AL, Kasperlik-Zaluska A, et al. Consensus statement on the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with primary adrenal insufficiency. J Intern Med. 2014;275(2):104–115. doi: 10.1111/joim.12162. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Lu L, Lu Z, Chen S, Zhu H, Pan H, Dduan L, Yang H, Wang L, Yuan T, et al. Etiology and clinical features of primary adrenal insufficiency. Natl Med J China. 2020;12(100):915–921. - PubMed
-
- The writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Disease in China: Report on Cardiovascular health and diseases burden in china: an updated summary of 2020. Chin Circ J 2021, 36(06):521–545.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

