Written Asthma Action Plan Improves Asthma Control and the Quality of Life among Pediatric Asthma Patients in Malaysia: A Randomized Control Trial
- PMID: 36709960
- PMCID: PMC9887449
- DOI: 10.4082/kjfm.22.0016
Written Asthma Action Plan Improves Asthma Control and the Quality of Life among Pediatric Asthma Patients in Malaysia: A Randomized Control Trial
Abstract
Background: A written asthma action plan (WAAP) is one of the treatment strategies to achieve good asthma control in children.
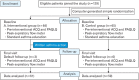
Methods: This randomized controlled trial was conducted to observe the effect of WAAP on asthma control and quality of life using the Asthma Control Questionnaire and Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (PAQLQ) at baseline and after 3 months. A repeated measure analysis of variance was used to analyze the mean score difference between the two groups.
Results: There was no significant difference in mean score for asthma control at baseline between groups (F[degree of freedom (df)]=1.17 [1, 119], P=0.282). However, at 3 months, a significant difference in mean scores between groups was observed (F[df]=7.32 [1, 119], P=0.008). The mean±standard deviation (SD) scores in the intervention and control groups were 0.96±0.53 and 1.21±0.49, respectively. For the analysis of the PAQLQ, no significant difference was observed in the mean score for the quality of life baseline in both groups. There were significant mean score changes for the quality of life (F[df]=10.9 [1, 119], P=0.001) at 3 months follow-up, where those in the intervention group scored a mean±SD score of 6.19±0.45, and those in the control group scored 5.94±0.38. A time-group interaction analysis using repeated-measures analysis of variance showed significant differences in mean score changes (F[df]=5.03 [1, 116], P=0.027) and (F[df]=11.55 [1, 116], P=0.001) where a lower mean score was observed in the intervention group, indicating better asthma control and quality of life, respectively. A significant (P<0.001) negative Pearson correlation between asthma control and quality of life (-0.65) indicated a moderate correlation.
Conclusion: WAAP, along with standard asthma treatment, improves asthma care.
Keywords: Asthma; Asthma Control; Pediatric; Written Asthma Action Plan.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvement of quality of life in a family of a child with asthma after using the Written Asthma Action Plan (WAAP).J Family Med Prim Care. 2023 Jul;12(7):1336-1341. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1828_22. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Family Med Prim Care. 2023. PMID: 37649773 Free PMC article.
-
Providing individualized written asthma action plans during the pediatric emergency department visit.J Asthma. 2021 Jun;58(6):819-824. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2020.1731824. Epub 2020 Mar 6. J Asthma. 2021. PMID: 32066290 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing Written Versus Pictorial Asthma Action Plans to Improve Asthma Management and Health Outcomes Among Children and Adolescents: Protocol of a Pilot and Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2019 Jun 17;8(6):e11733. doi: 10.2196/11733. JMIR Res Protoc. 2019. PMID: 31210140 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with ownership and use of written asthma action plans in North-West Melbourne.Prim Care Respir J. 2004 Dec;13(4):211-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pcrj.2004.04.002. Prim Care Respir J. 2004. PMID: 16701671 Free PMC article.
-
PELICAN: a cluster-randomized controlled trial in Dutch general practices to assess a self-management support intervention based on individual goals for children with asthma.J Asthma. 2015 Mar;52(2):211-9. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2014.952439. Epub 2014 Aug 28. J Asthma. 2015. PMID: 25166455 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Implementation of written asthma action plan among asthma patients in Türkiye: a multicenter, cross-sectional, descriptive study.Turk J Med Sci. 2024 Aug 19;54(6):1281-1285. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5910. eCollection 2024. Turk J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39734334 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of asthma education grounded in virtual reality technology upon the quality of life of pediatric patients with bronchial asthma.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 5;13:1588562. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1588562. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40538930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeh HY, Ma WF, Huang JL, Hsueh KC, Chiang LC. Evaluating the effectiveness of a family empowerment program on family function and pulmonary function of children with asthma: a randomized control trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2016;60:133–44. - PubMed
-
- Fischer GB, Camargos PA. Paediatric asthma management in developing countries. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2002;3:285–91. - PubMed
-
- Kotwani A, Chhabra SK. Effect of patient education and standard treatment guidelines on asthma control: an intervention trial. WHO South East Asia J Public Health. 2012;1:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health Malaysia . Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Childhood Asthma Malaysia. Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia; 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous