Therapeutic effect of oral quercetin in hamsters infected with Leishmania Viannia braziliensis
- PMID: 36710981
- PMCID: PMC9880276
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1059168
Therapeutic effect of oral quercetin in hamsters infected with Leishmania Viannia braziliensis
Abstract
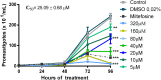
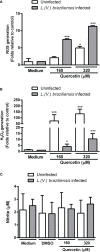
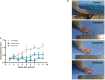
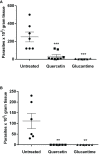
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of intracellular protozoa of the genus Leishmania that present manifestations ranging from cutaneous ulcers to the fatal visceral form. Leishmania Viannia braziliensis is an important species associated with American tegumentary leishmaniasis and the main agent in Brazil, with variable sensitivity to available drugs. The search for new therapeutic alternatives to treat leishmaniasis is an urgent need, especially for endemic countries. Not only is quercetin well known for its antioxidant activity in radical scavenging but also several other biological effects are described, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and pro-oxidant activities. This study aimed to investigate the flavonoid quercetin's therapeutic potential in L. (V.) braziliensis infection. Quercetin showed antiamastigote (IC50 of 21 ± 2.5 µM) and antipromastigote (25 ± 0.7 µM) activities and a selectivity index of 22. The treatment of uninfected or L. (V.) braziliensis-infected macrophages with quercetin increased reactive oxygen species (ROS)/H202 generation without altering Nitric Oxide (NO) production. Oral treatment with quercetin of infected hamsters, starting at 1 week of infection for 8 weeks, reduced the lesion thickness (p > 0.01) and parasite load (p > 0.001). The results of this study suggest that the antiamastigote activity of the flavonoid quercetin in vitro is associated, at least in part, with the modulation of ROS production by macrophages. The efficacy of oral quercetin treatment in hamsters infected with L. (V.) braziliensis was presented for the first time and shows its promising therapeutic potential.
Keywords: Leishmania braziliensis; hamsters; oral treatment; quercetin; reactive species of oxygen.
Copyright © 2023 Santos, Da Silva, Brito, Inácio, Ventura, Mendes, Azevedo, Siqueira, Almeida-Amaral, Dutra and Da-Silva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abbaszadeh S., Rashidipour M., Khosravi P., Shahryarhesami S., Ashrafi B., Kaviani M., et al. . (2020). Biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial and epigenetic effects of novel chitosan-based quercetin nanohydrogel in human cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed 15, 5963–5975. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S263013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behling E. B., Sendão M. C., Francescato H. D. C., Antunes L. M. G., Bianchi M. D. L. P. (2004). Flavonóide Quercetina : Aspectos gerais e. Alimentos e Nutrição - Braz. J. Food Nutr. 15, 285–292.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

