Complete Remission of Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy in Copper Smelting and Purification Workers: A Case Report
- PMID: 36711071
- PMCID: PMC9879774
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S398275
Complete Remission of Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy in Copper Smelting and Purification Workers: A Case Report
Abstract
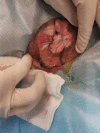
Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC) is the most frequent vulvar neoplasia, with invasiveness and metastasis. Typically, surgery is the preferred treatment. Radiotherapy is commonly used for unresectable locally advanced tumors and for early-stage patients who are at risk of serious complications from surgery or have a severe concomitant disease that prevents them from undergoing surgery. Compared to external irradiation, three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT), and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), various studies using volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) alone in early-stage VSCC have been reported rarely. In this case, the patient had a large skin lesion and no lymph node metastasis. Surgical excision would seriously affect the urinary function and vulvar shape, so radical radiotherapy was given. To ensure the radiation dose for the radical treatment effect and to avoid high-dose radiation to normal organs, the volumetric intensity-modulated radiotherapy technique was chosen. After treatment, the patient's vulvar appearance returned to normal, and the tumor achieved complete remission without further surgery or chemotherapy, with no local recurrence or associated toxic side effects. This suggests that the efficacy of VMAT alone in early-stage VSCC is accurate and worthy of clinical promotion. The patient had been engaged in copper smelting and purification for many years, and it is unusual for her to have skin lesions with such a large surface area. In conjunction with her previous history of nasal basal cell carcinoma, the mechanism of oxidative stress during metal exposure should be further clinically examined, as it may be crucial in the formation and progression of malignancies.
Keywords: metal; oxidative stress; radiotherapy; skin malignancies; squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2023 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




References
-
- Gynecological Tumor Committee of China Anti-Cancer Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of vulvar malignancies (2021 edition). China Oncol. 2021;31(6):533–545. doi:10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2021.06.11 - DOI
-
- Alishahi M, Malekirad A, Mandegary A, et al. A study on oxidative stress, hematological and biochemical parameters in copper smelter workers. Toxin Rev. 2020;8:1–6. doi:10.1080/15569543.2017.1278708 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

