Somatosensory ECoG-based brain-machine interface with electrical stimulation on medial forebrain bundle
- PMID: 36711163
- PMCID: PMC9873859
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-022-00256-6
Somatosensory ECoG-based brain-machine interface with electrical stimulation on medial forebrain bundle
Abstract
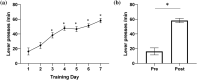
Brain-machine interface (BMI) provides an alternative route for controlling an external device with one's intention. For individuals with motor-related disability, the BMI technologies can be used to replace or restore motor functions. Therefore, BMIs for movement restoration generally decode the neural activity from the motor-related brain regions. In this study, however, we designed a BMI system that uses sensory-related neural signals for BMI combined with electrical stimulation for reward. Four-channel electrocorticographic (ECoG) signals were recorded from the whisker-related somatosensory cortex of rats and converted to extract the BMI signals to control the one-dimensional movement of a dot on the screen. At the same time, we used operant conditioning with electrical stimulation on medial forebrain bundle (MFB), which provides a virtual reward to motivate the rat to move the dot towards the desired center region. The BMI task training was performed for 7 days with ECoG recording and MFB stimulation. Animals successfully learned to move the dot location to the desired position using S1BF neural activity. This study successfully demonstrated that it is feasible to utilize the neural signals from the whisker somatosensory cortex for BMI system. In addition, the MFB electrical stimulation is effective for rats to learn the behavioral task for BMI.
Keywords: Brain plasticity; Brain–machine interface; Deep brain stimulation; Somatosensory cortex; Virtual reward.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Ajiboye AB, Willett FR, Young DR, Memberg WD, Murphy BA, Miller JP, Walter BL, Sweet JA, Hoyen HA, Keith MW, Peckham PH, Simeral JD, Donoghue JP, Hochberg LR, Kirsch RF. Restoration of reaching and grasping movements through brain-controlled muscle stimulation in a person with tetraplegia: a proof-of-concept demonstration. Lancet. 2017;389:1821–1830. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30601-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Otto KJ, Vetter RJ, Marzullo TC, Kipke DR. Brain–machine interfaces in rat motor cortex: implications of adaptive decoding algorithms. In: Walker LJ, Strock JL, editors. 1st international IEEE EMBS conference on neural engineering 2003. 2003. p. 100–103. 10.1109/CNE.2003.1196766.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
