This is a preprint.
MNK1 and MNK2 expression in the human dorsal root and trigeminal ganglion
- PMID: 36711529
- PMCID: PMC9881964
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.01.04.522773
MNK1 and MNK2 expression in the human dorsal root and trigeminal ganglion
Update in
-
MNK1 and MNK2 Expression in the Human Dorsal Root and Trigeminal Ganglion.Neuroscience. 2023 Apr 1;515:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.01.039. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 36764601
Abstract
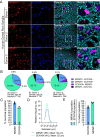
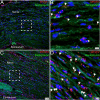
Mitogen activated protein kinase interacting kinases (MNK) 1 and 2 are serine/threonine protein kinases that play an important role in translation of mRNAs through their phosphorylation of the RNA 5’-cap binding protein, eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF) 4E. These kinases are downstream targets for mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs), extracellular activity regulated protein kinase (ERK) and p38. MNKs have been implicated in the sensitization of peripheral nociceptors of the dorsal root and trigeminal ganglion (DRG and TG) using transgenic mouse lines and through the use of specific inhibitors of MNK1 and MNK2. While specific knockout of the Mknk1 gene suggests that it is the key isoform for regulation of nociceptor excitability and nociceptive behaviors in mice, both MKNK1 and MKNK2 genes are expressed in the DRG and TG of mice and humans based on RNA sequencing experiments. Single cell sequencing in mice suggests that Mknk1 and Mknk2 may be expressed in different populations of nociceptors. We sought to characterize mRNA expression in human DRG and TG for both MNK1 and MNK2. Our results show that both genes are expressed by nearly all neurons in both human ganglia with expression in other cell types as well. Our findings provide evidence that MNK1 and MNK2 are expressed by human nociceptors and suggest that efforts to pharmacologically target MNKs for pain would likely be translatable due its conserved expression in both species.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
JJS is an employee of 4E Therapeutics and TJP is a founder of 4E Therapeutics, a company developing MNK inhibitors for pain treatment. SS, JJS and TJP are inventors on patents related to MNK inhibition for pain treatment
Figures



References
-
- Aguilar-Valles A, Haji N, De Gregorio D, Matta-Camacho E, Eslamizade MJ, Popic J, Sharma V, Cao R, Rummel C, Tanti A, Wiebe S, Nunez N, Comai S, Nadon R, Luheshi G, Mechawar N, Turecki G, Lacaille JC, Gobbi G, Sonenberg N (2018) Translational control of depression-like behavior via phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Nat Commun 9:2459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN (1996) A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature 379:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Buxade M, Parra-Palau JL, Proud CG (2008) The Mnks: MAP kinase-interacting kinases (MAP kinase signal-integrating kinases). Front Biosci 13:5359–5373. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
