This is a preprint.
Non-catalytic role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mesenchymal cell migration through non-canonical induction of p85β/AP-2-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 36712134
- PMCID: PMC9881872
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.12.31.522383
Non-catalytic role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mesenchymal cell migration through non-canonical induction of p85β/AP-2-mediated endocytosis
Update in
-
Non-catalytic role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mesenchymal cell migration through non-canonical induction of p85β/AP2-mediated endocytosis.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 23;15(1):2612. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46855-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38521786 Free PMC article.
Abstract
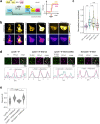
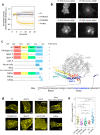
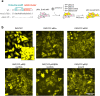
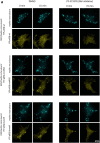
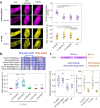
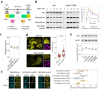
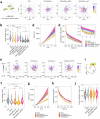
Class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) galvanizes fundamental cellular processes such as migration, proliferation, and differentiation. To enable multifaceted roles, the catalytic subunit p110 utilizes a multidomain, regulatory subunit p85 through its inter SH2 domain (iSH2). In cell migration, their product PI(3,4,5)P3 generates locomotive activity. While non-catalytic roles are also implicated, underlying mechanisms and its relationship to PI(3,4,5)P3 signaling remain elusive. Here, we report that a disordered region of iSH2 contains previously uncharacterized AP-2 binding motifs which can trigger clathrin and dynamin-mediated endocytosis independent of PI3K catalytic activity. The AP-2 binding motif mutants of p85 aberrantly accumulate at focal adhesions and upregulate both velocity and persistency in fibroblast migration. We thus propose the dual functionality of PI3K in the control of cell motility, catalytic and non-catalytic, arising distinctly from juxtaposed regions within iSH2.
Figures







References
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B., Guillermet-Guibert J., Graupera M. & Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 11, 329–341 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Bilanges B., Posor Y. & Vanhaesebroeck B. PI3K isoforms in cell signalling and vesicle trafficking. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 20, 515–534 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
