Dietary coated essential oil and organic acid mixture supplementation improves health of broilers infected with avian pathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 36712401
- PMCID: PMC9868345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.09.010
Dietary coated essential oil and organic acid mixture supplementation improves health of broilers infected with avian pathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
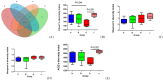
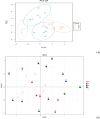
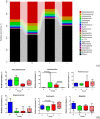
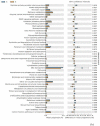
Colibacillosis caused by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) is a very prevalent disease in poultry farms in China. The exploration of effective non-antibiotic substances is of great significance for the control of APEC infections. This experiment evaluated the efficacy of coated essential oil and organic acid (EOA) supplementation to prevent E. coli O78 infection in broiler chickens. A total of 288 one-day-old male broiler chicks were randomly distributed into 4 groups with 6 replicates per group. Chickens were fed a diet either supplemented with EOA (500 mg/kg feed) or not, and either uninfected or infected with E. coli O78 intratracheally. Results showed that E. coli O78 infection reduced body weight gain, increased mortality and the ratio of feed to gain along with cecal and liver E. coli load, damaged gut mucosa, induced local and systemic inflammation, and altered cecal microbial composition, diversity and function (P < 0.05). Supplemental EOA improved feed conversion efficiency, lowered gross lesion scores and cecal E. coli population, enhanced intestinal goblet cells and serum IgG concentration, and tended to decrease serum IL-12 production (P < 0.05). Essential oil and organic acid addition downregulated IFN-γ mRNA, tended to decrease mucin-2 mRNA levels while upregulating IL-10 mRNA, and tended to increase ZO-1 gene expression in the jejuna of infected birds at 7 d after E. coli O78 challenge (P < 0.05). The 16S rRNA gene sequencing indicated that both EOA addition and E. coli O78 challenge altered the diversity and composition of the cecal microbiota community. Furthermore, infected birds fed EOA showed decreased Bacteroidetes and genus Lactobacillus abundance compared with the infected control. LEfSe analysis showed that Firmicutes, Ruminococcaceae, Clostridiales, Clostridia, Lactobacillus, Lactobacilaceae, and cc-115 were enriched in the non-infected but EOA-treated group (P < 0.05). Collectively, dietary EOA supplementation could mildly alleviate E. coli-induced gut injury and inflammation.
Keywords: Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli; Broiler chicken; Encapsulated essential oil and organic acid mixture; Health.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, and there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the content of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Abu-Basha E.A., Gharaibeh S.M., Thabet A.M. In vitro susceptibility of resistant Escherichia coli field isolates to antimicrobial combinations. J Appl Poultry Res. 2012;21(3):595–602.
-
- Abudabos A.M., Al-Mufarrej S.I. Effects of organic acid supplementation on antioxidant capacity and immune responses of broilers challenged orally with Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Typhimurium. South Afr J Anim Sci. 2014;44(4):342–349.
-
- Adaszyńska-Skwirzyńska M., Szczerbińska D. The antimicrobial activity of lavender essential oil (Lavandula angustifolia) and its influence on the production performance of broiler chickens. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. 2018;102(4):1020–1025. - PubMed
-
- Adil S., Banday T., Bhat G.A., Salahuddin M., Raquib M., Shanaz S. Response of broiler chicken to dietary supplementation of organic acids. J Cent Eur Agric. 2011;12(3):498–508.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

