The potential roles of dental pulp stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
- PMID: 36712432
- PMCID: PMC9874689
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1098857
The potential roles of dental pulp stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
Abstract
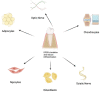
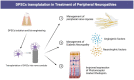
Peripheral nerve diseases are significantly correlated with severe fractures or trauma and surgeries, leading to poor life quality and impairment of physical and mental health. Human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) are neural crest stem cells with a strong multi-directional differentiation potential and proliferation capacity that provide a novel cell source for nerve regeneration. DPSCs are easily extracted from dental pulp tissue of human permanent or deciduous teeth. DPSCs can express neurotrophic and immunomodulatory factors and, subsequently, induce blood vessel formation and nerve regeneration. Therefore, DPSCs yield valuable therapeutic potential in the management of peripheral neuropathies. With the purpose of summarizing the advances in DPSCs and their potential applications in peripheral neuropathies, this article reviews the biological characteristics of DPSCs in association with the mechanisms of peripheral nerve regeneration.
Keywords: Schwann cells; dental pulp stem cells; neuron; neurotrophic factors; peripheral nerve diseases.
Copyright © 2023 Fu, Li, Jin, Dong, Zhou, Alhaskawi, Wang, Lai, Yao, Ezzi, Kota, Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla, Chen and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources