Expression of miR-320 and miR-204 in myocardial infarction and correlation with prognosis and degree of heart failure
- PMID: 36712879
- PMCID: PMC9873962
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1094332
Expression of miR-320 and miR-204 in myocardial infarction and correlation with prognosis and degree of heart failure
Abstract
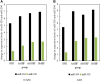
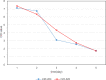
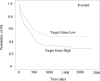
Myocardial infarction is a very dangerous cardiovascular disease with a high mortality rate under the modern developed medical technology. miRNA is a small molecule regulatory RNA discovered in recent years, which can play an important role in many cancers and other diseases. Medical data, machine learning and medical care strategies supporting the Internet of Things (IoMT) have certain applications in the treatment of myocardial infarction. However, the specific pathogenesis of myocardial infarction is still unclear. Therefore, this paper aimed to explore the expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 in myocardial infarction and used the expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 to predict the prognosis of patients with myocardial infarction. In order to discuss the expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 in myocardial infarction in more detail. In this paper, 40 patients in the trial period were selected for clinical research, and 10 patients with normal cardiac function were selected in NHF group as control group. 10 patients with heart failure were selected as AMHF group. 10 patients with acute myocardial infarction were selected as AMNHF group. 10 patients with heart failure after old myocardial infarction were selected as OMHF group. AMHF group, AMNHF group and OMHF group were taken as the case group. This paper analyzed the difference of miR between different groups and determined that there were significant differences in the expression of miR-320 and miR-204 between different groups. Finally, the expression and prognosis of miR-320 and miR-204 in myocardial infarction were analyzed. The analysis results showed that the expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 can inhibit the activity of myocardial cells. On the fifth day, the corresponding expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 reduced the optical density of myocardial cells to 1.75 and 1.76, which was significantly lower than that on the first day. Moreover, excessive miR-320 expression and excessive miR-204 expression can increase the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells. The above results indicated that the high expression of microRNA-320 and microRNA-204 can be a bad prognostic factor in patients with myocardial infarction, showing that medical data, machine learning and medical care strategies supporting IoMT can play a role in the treatment of myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is urgent to understand the pathogenesis of heart failure after myocardial infarction and find new treatment schemes to improve the positive prognosis.
Keywords: healthcare strategy; internet of things (IoMT) medical data; medical data; miR-320 and miR-204; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Guo, Lu, Huang, Yang and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
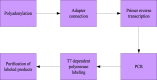
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

