COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from chest CT images based on CAPA-ResUNet
- PMID: 36713026
- PMCID: PMC9874448
- DOI: 10.1002/ima.22819
COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from chest CT images based on CAPA-ResUNet
Abstract
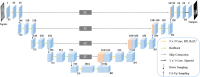
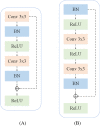
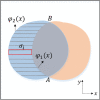
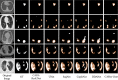
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic has devastating effects on personal health around the world. It is significant to achieve accurate segmentation of pulmonary infection regions, which is an early indicator of disease. To solve this problem, a deep learning model, namely, the content-aware pre-activated residual UNet (CAPA-ResUNet), was proposed for segmenting COVID-19 lesions from CT slices. In this network, the pre-activated residual block was used for down-sampling to solve the problems of complex foreground and large fluctuations of distribution in datasets during training and to avoid gradient disappearance. The area loss function based on the false segmentation regions was proposed to solve the problem of fuzzy boundary of the lesion area. This model was evaluated by the public dataset (COVID-19 Lung CT Lesion Segmentation Challenge-2020) and compared its performance with those of classical models. Our method gains an advantage over other models in multiple metrics. Such as the Dice coefficient, specificity (Spe), and intersection over union (IoU), our CAPA-ResUNet obtained 0.775 points, 0.972 points, and 0.646 points, respectively. The Dice coefficient of our model was 2.51% higher than Content-aware residual UNet (CARes-UNet). The code is available at https://github.com/malu108/LungInfectionSeg.
Keywords: COVID‐19; area loss function; computed tomography (CT) image segmentation; deep learning; pre‐activated residual block.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CARes-UNet: Content-aware residual UNet for lesion segmentation of COVID-19 from chest CT images.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):7127-7140. doi: 10.1002/mp.15231. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34528263 Free PMC article.
-
A novel adaptive cubic quasi-Newton optimizer for deep learning based medical image analysis tasks, validated on detection of COVID-19 and segmentation for COVID-19 lung infection, liver tumor, and optic disc/cup.Med Phys. 2023 Mar;50(3):1528-1538. doi: 10.1002/mp.15969. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36057788 Free PMC article.
-
Automated deep learning-based segmentation of COVID-19 lesions from chest computed tomography images.Pol J Radiol. 2022 Aug 26;87:e478-e486. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2022.119027. eCollection 2022. Pol J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36091652 Free PMC article.
-
Research on CT Lung Segmentation Method of Preschool Children based on Traditional Image Processing and ResUnet.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 10;2022:7321330. doi: 10.1155/2022/7321330. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36262868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attention-UNet architectures with pretrained backbones for multi-class cardiac MR image segmentation.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Jan;49(1 Pt C):102129. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102129. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37866419 Review.
References
-
- Organization WH . Weekly epidemiological update on COVID‐19. 2022. Accessed January 6, 2022. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/situatio....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
