Modifiable factors for migraine prophylaxis: A mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 36713835
- PMCID: PMC9878312
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1010996
Modifiable factors for migraine prophylaxis: A mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
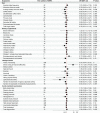
Objective: To examine the causal effect of potentially modifiable risk factors contributing to migraine pathogenesis. Methods: We performed Mendelian randomization analyses and acquired data from United Kingdom Biobank, FinnGen Biobank, and the MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure. An inverse-variance weighted (IVW) model was used to examine the relationship between 51 potentially modifiable risk factors and migraine in 3215 participants with migraine without aura (MwoA), 3541 participants with migraine with aura (MwA), and 176,107 controls. We adopted a Bonferroni-corrected threshold of p = 9.8 × 10-4 (.05 divided by 51 exposures) as a sign of significant effect, and a p < .05 was considered as the sign of a suggestive association. Results: More years of schooling significantly correlated with lower odds of MwoA pathogenesis (OR .57 [95%CI .44 to .75], p < .0001). More vitamin B12 intake (OR .49 [95%CI .24 to .99], p = .046) and lower level of stress [OR 8.17 (95%CI 1.5 to 44.36), p = .015] or anxiety disorder (OR 1.92 × 109 [95%CI 8.76 to 4.23*1017], p = .029) were suggestive to be correlated lower odds of MwoA pathogenesis. More coffee intake (OR .39 [95%CI .22 to .7], p = .001), lower level of eicosapentaenoic acid status (OR 2.54 [95%CI 1.03 to 6.26], p = .043), and more light physical activity (OR .09 [95%CI .01 to .94], p = .046) were suggestive to be associated with lower odds of MwA. Conclusion: The years of schooling, light physical activity, vitamin B12 intake, and coffee intake were the protective factors for migraine; stress, anxiety, and eicosapentaenoic acid status were harmful factors. Interventions could be developed based on modifying these factors for migraine prophylaxis.
Keywords: mendelian randomization; migraine prophylaxis; modifiable risk factors; public health; schooling.
Copyright © 2023 Zheng, Shi, Liang, Lu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bowden J., Del Greco M. F., Minelli C., Davey Smith G., Sheehan N. A., Thompson J. R. (2016). Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample mendelian randomization analyses using MR-egger regression: The role of the I2 statistic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 45, 1961–1974. 10.1093/ije/dyw220 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

