Multiview Deep Forest for Overall Survival Prediction in Cancer
- PMID: 36714327
- PMCID: PMC9876666
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/7931321
Multiview Deep Forest for Overall Survival Prediction in Cancer
Abstract
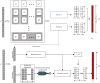
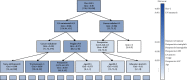
Overall survival (OS) in cancer is crucial for cancer treatment. Many machine learning methods have been applied to predict OS, but there are still the challenges of dealing with multiview data and overfitting. To overcome these problems, we propose a multiview deep forest (MVDF) in this paper. MVDF can learn the features of each view and fuse them with integrated learning and multiple kernel learning. Then, a gradient boost forest based on the information bottleneck theory is proposed to reduce redundant information and avoid overfitting. In addition, a pruning strategy for a cascaded forest is used to limit the impact of outlier data. Comprehensive experiments have been carried out on a data set from West China Hospital of Sichuan University and two public data sets. Results have demonstrated that our method outperforms the compared methods in predicting overall survival.
Copyright © 2023 Qiucen Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- N C Institute. Understanding Cancer Prognosis, Website . February 2022, https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/diagnosis-staging/prognosis/
-
- Zhao Z., Bai L., Zhang Y., Han J. Classification via semi-supervised multirandom subspace sparse representation. Signal, Image and Video Processing . 2019;13(7):1387–1394. doi: 10.1007/s11760-019-01467-8. - DOI
-
- Che S., Peng H., Sun L., Chen Y., He L. Federated multi-view learning for private medical data integration and analysis. 2021. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.01603.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

