DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap
- PMID: 36714378
- PMCID: PMC9869848
- DOI: 10.1038/s41570-022-00456-9
DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap.Nat Rev Chem. 2023 Aug;7(8):590. doi: 10.1038/s41570-023-00521-x. Nat Rev Chem. 2023. PMID: 37391543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
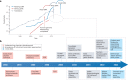
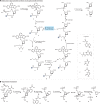
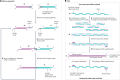
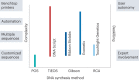
Synthetic DNA is of increasing demand across many sectors of research and commercial activities. Engineering biology, therapy, data storage and nanotechnology are set for rapid developments if DNA can be provided at scale and low cost. Stimulated by successes in next generation sequencing and gene editing technologies, DNA synthesis is already a burgeoning industry. However, the synthesis of >200 bp sequences remains unaffordable. To overcome these limitations and start writing DNA as effectively as it is read, alternative technologies have been developed including molecular assembly and cloning methods, template-independent enzymatic synthesis, microarray and rolling circle amplification techniques. Here, we review the progress in developing and commercializing these technologies, which are exemplified by innovations from leading companies. We discuss pros and cons of each technology, the need for oversight and regulatory policies for DNA synthesis as a whole and give an overview of DNA synthesis business models.
Keywords: DNA; Synthetic biology.
© Crown 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

